Structural effects of oncogenic PI3Kα mutations
- PMID: 20593314
- PMCID: PMC3172713
- DOI: 10.1007/82_2010_53
Structural effects of oncogenic PI3Kα mutations
Abstract
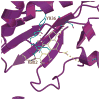
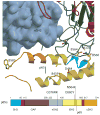
Physiological activation of PI3Kα is brought about by the release of the inhibition by p85 when the nSH2 binds the phosphorylated tyrosine of activated receptors or their substrates. Oncogenic mutations of PI3Kα result in a constitutively activated enzyme that triggers downstream pathways that increase tumor aggressiveness and survival. Structural information suggests that some mutations also activate the enzyme by releasing p85 inhibition. Other mutations work by different mechanisms. For example, the most common mutation, His1047Arg, causes a conformational change that increases membrane association resulting in greater accessibility to the substrate, an integral membrane component. These effects are examples of the subtle structural changes that result in increased activity. The structures of these and other mutants are providing the basis for the design of isozyme-specific, mutation-specific inhibitors for individualized cancer therapies.
Figures
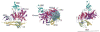



Similar articles
-
Capitalizing on tumor genotyping: towards the design of mutation specific inhibitors of phosphoinsitide-3-kinase.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2011;51(1):273-9. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2011. PMID: 21035489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of PI3Kα by physiological effectors and by oncogenic mutations: structural and dynamic effects.Biophys Rev. 2014 Mar 1;6(1):89-95. doi: 10.1007/s12551-013-0131-1. Biophys Rev. 2014. PMID: 25309634 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the oncogenic effects of PIK3CA mutations from the structure of p110alpha/p85alpha.Cell Cycle. 2008 May 1;7(9):1151-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.9.5817. Epub 2008 Feb 27. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18418043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic mutations weaken the interactions that stabilize the p110α-p85α heterodimer in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α.FEBS J. 2015 Sep;282(18):3528-42. doi: 10.1111/febs.13365. Epub 2015 Jul 24. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 26122737 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K Driver Mutations: A Biophysical Membrane-Centric Perspective.Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 15;81(2):237-247. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0911. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33046444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AutoEpiCollect, a Novel Machine Learning-Based GUI Software for Vaccine Design: Application to Pan-Cancer Vaccine Design Targeting PIK3CA Neoantigens.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Mar 27;11(4):322. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11040322. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671743 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the subcellular distribution of oncogenic phosphoinositide 3-kinase using microinjection into live cells.Biosci Rep. 2014 Apr 1;34(2):e00104. doi: 10.1042/BSR20130133. Print 2014 Apr 1. Biosci Rep. 2014. PMID: 27919038 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Perturbations due to Mutation (H1047R) in Phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3Kα) and Its Involvement in Oncogenesis: An in Silico Insight.ACS Omega. 2019 Sep 20;4(14):15815-15823. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b01439. eCollection 2019 Oct 1. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31592171 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of an isolated p110α subunit of PI3Kα permits crystallization and provides a platform for structure-based drug design.Protein Sci. 2014 Oct;23(10):1332-40. doi: 10.1002/pro.2517. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 25043846 Free PMC article.
-
PIK3CA C2 Domain Deletions Hyperactivate Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), Generate Oncogene Dependence, and Are Exquisitely Sensitive to PI3Kα Inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 15;24(6):1426-1435. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2141. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29284706 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

