FGF-23: More than a regulator of renal phosphate handling?
- PMID: 20593414
- PMCID: PMC3153315
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.170
FGF-23: More than a regulator of renal phosphate handling?
Abstract
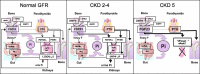
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) is likely to be the most important regulator of phosphate homeostasis, which mediates its functions through FGF receptors and the coreceptor Klotho. Besides reducing expression of the sodium-phosphate cotransporters NPT2a and NPT2c in the proximal tubules, FGF-23 inhibits the renal 1α-hydroxylase and stimulates the 24-hydroxylase, and it appears to reduce parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion in short-term studies. FGF-23 synthesis and secretion by osteocytes and osteoblasts is upregulated through 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,25(OH)(2)D(3)] and through an increased dietary phosphate intake. FGF-23 levels are elevated or inappropriately normal in patients with tumor-induced osteomalacia and several inherited hypophosphatemic disorders, but the most significant increases are found in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). During the early stages of CKD, increased FGF-23 production enhances urinary phosphate excretion and thus prevents the development of hyperphosphatemia, reduces the circulating levels of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3), and therefore contributes to the development of secondary hyperparathyroidism. In patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), FGF-23 levels can be extremely high and were shown to be predictors of bone mineralization, left ventricular hypertrophy, vascular calcification, and mortality. It remains to be determined, however, whether FGF-23 represents simply a sensitive biomarker of an abnormal phosphate homeostasis or has, independent of serum phosphate levels, potentially negative "off-target" effects. Nonetheless, reducing the production and/or the biologic activity of FGF-23 may be an important therapeutic goal for this patient population.
Figures
References
-
- Potts JT, Jr, Bringhurst FR, Gardella TJ, Nussbaum SR, Segre GV, Kronenberg HM. Parathyroid hormone: physiology, chemistry, biosynthesis, secretion, metabolism, and mode of action. In: DeGroot LJ, editor. Endocrinology. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1996. pp. 920–965.
-
- Gardella T, Jüppner H, Brown E, Kronenberg H, Potts J., Jr. Parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide in the regulation of calcium homeostasis and bone development. In: DeGroot L, Jameson J, editors. Endocrinology. 5th ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2010.
-
- St-Arnaud R, Demay MB. Vitamin D biology. In: Glorieux FH, Pettifor H, Jüppner H, editors. Pediatric Bone: Biology and Diseases. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2003. pp. 193–216.
-
- White KE, Larsson TE, Econs MJ. The roles of specific genes implicated as circulating factors involved in normal and disordered phosphate homeostasis: frizzled related protein-4, matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein, and fibroblast growth factor 23. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:221–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

