Evidence from FTIR difference spectroscopy of an extensive network of hydrogen bonds near the oxygen-evolving Mn(4)Ca cluster of photosystem II involving D1-Glu65, D2-Glu312, and D1-Glu329
- PMID: 20593803
- PMCID: PMC2917469
- DOI: 10.1021/bi100730d
Evidence from FTIR difference spectroscopy of an extensive network of hydrogen bonds near the oxygen-evolving Mn(4)Ca cluster of photosystem II involving D1-Glu65, D2-Glu312, and D1-Glu329
Abstract
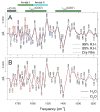
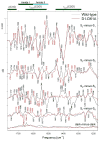
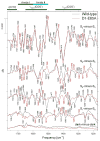
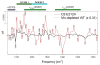
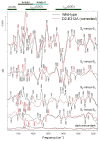
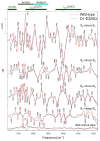
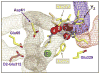
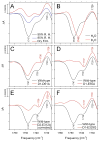
Analyses of the refined X-ray crystallographic structures of photosystem II (PSII) at 2.9-3.5 A have revealed the presence of possible channels for the removal of protons from the catalytic Mn(4)Ca cluster during the water-splitting reaction. As an initial attempt to verify these channels experimentally, the presence of a network of hydrogen bonds near the Mn(4)Ca cluster was probed with FTIR difference spectroscopy in a spectral region sensitive to the protonation states of carboxylate residues and, in particular, with a negative band at 1747 cm(-1) that is often observed in the S(2)-minus-S(1) FTIR difference spectrum of PSII from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. On the basis of its 4 cm(-1) downshift in D(2)O, this band was assigned to the carbonyl stretching vibration (C horizontal lineO) of a protonated carboxylate group whose pK(a) decreases during the S(1) to S(2) transition. The positive charge that forms on the Mn(4)Ca cluster during the S(1) to S(2) transition presumably causes structural perturbations that are transmitted to this carboxylate group via electrostatic interactions and/or an extended network of hydrogen bonds. In an attempt to identify the carboxylate group that gives rise to this band, the FTIR difference spectra of PSII core complexes from the mutants D1-Asp61Ala, D1-Glu65Ala, D1-Glu329Gln, and D2-Glu312Ala were examined. In the X-ray crystallographic models, these are the closest carboxylate residues to the Mn(4)Ca cluster that do not ligate Mn or Ca and all are highly conserved. The 1747 cm(-1) band is present in the S(2)-minus-S(1) FTIR difference spectrum of D1-Asp61Ala but absent from the corresponding spectra of D1-Glu65Ala, D2-Glu312Ala, and D1-Glu329Gln. The band is also sharply diminished in magnitude in the wild type when samples are maintained at a relative humidity of </=85%. It is proposed that D1-Glu65, D2-Glu312, and D1-Glu329 participate in a common network of hydrogen bonds that includes water molecules and the carboxylate group that gives rise to the 1747 cm(-1) band. It is further proposed that the mutation of any of these three residues, or partial dehydration caused by maintaining samples at a relative humidity of <or=85%, disrupts the network sufficiently that the structural perturbations associated with the S(1) to S(2) transition are no longer transmitted to the carboxylate group that gives rise to the 1747 cm(-1) band. Because D1-Glu329 is located approximately 20 A from D1-Glu65 and D2-Glu312, the postulated network of hydrogen bonds must extend for at least 20 A across the lumenal face of the Mn(4)Ca cluster. The D1-Asp61Ala, D1-Glu65Ala, and D2-Glu312Ala mutations also appear to substantially decrease the fraction of PSII reaction centers that undergo the S(3) to S(0) transition in response to a saturating flash. This behavior is consistent with D1-Asp61, D1-Glu65, and D2-Glu312 participating in a dominant proton egress channel that links the Mn(4)Ca cluster with the thylakoid lumen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Participation of glutamate-354 of the CP43 polypeptide in the ligation of manganese and the binding of substrate water in photosystem II.Biochemistry. 2011 Jan 11;50(1):63-81. doi: 10.1021/bi1015937. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21114287 Free PMC article.
-
Network of hydrogen bonds near the oxygen-evolving Mn(4)CaO(5) cluster of photosystem II probed with FTIR difference spectroscopy.Biochemistry. 2014 Feb 18;53(6):1001-17. doi: 10.1021/bi401450y. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24460511
-
No evidence from FTIR difference spectroscopy that glutamate-189 of the D1 polypeptide ligates a Mn ion that undergoes oxidation during the S0 to S1, S1 to S2, or S2 to S3 transitions in photosystem II.Biochemistry. 2006 Jul 25;45(29):8801-11. doi: 10.1021/bi060583a. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16846223 Free PMC article.
-
FTIR studies of metal ligands, networks of hydrogen bonds, and water molecules near the active site Mn₄CaO₅ cluster in Photosystem II.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1847(1):19-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.07.007. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25038513 Review.
-
Mono-manganese mechanism of the photosystem II water splitting reaction by a unique Mn4Ca cluster.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jun;1767(6):484-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2007.03.012. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17490604 Review.
Cited by
-
D1-Asn-298 in photosystem II is involved in a hydrogen-bond network near the redox-active tyrosine YZ for proton exit during water oxidation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 8;292(49):20046-20057. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.815183. Epub 2017 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29046348 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallization of Photosystem II for Time-Resolved Structural Studies Using an X-ray Free Electron Laser.Methods Enzymol. 2015;557:459-82. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Apr 18. Methods Enzymol. 2015. PMID: 25950978 Free PMC article.
-
Structural dynamics in the water and proton channels of photosystem II during the S2 to S3 transition.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 11;12(1):6531. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26781-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34764256 Free PMC article.
-
Participation of glutamate-354 of the CP43 polypeptide in the ligation of manganese and the binding of substrate water in photosystem II.Biochemistry. 2011 Jan 11;50(1):63-81. doi: 10.1021/bi1015937. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21114287 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Removal of External Proteins PsbO, PsbP and PsbQ on Flash-Induced Molecular Oxygen Evolution and Its Biphasicity in Tobacco PSII.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 8;46(7):7187-7218. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070428. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferreira KN, Iverson TM, Maghlaoui K, Barber J, Iwata S. Architecture of the Photosynthetic Oxygen-Evolving Center. Science. 2004;303:1831–1838. - PubMed
-
- Loll B, Kern J, Saenger W, Zouni A, Biesiadka J. Towards Complete Cofactor Arrangement in the 3.0 Å Resolution Structure of Photosystem II. Nature. 2005;438:1040–1044. - PubMed
-
- Kern J, Biesiadka J, Loll B, Saenger W, Zouni A. Structure of the Mn4-Ca Cluster as Derived from X-ray Diffraction. Photosyn Res. 2007;92:389–405. - PubMed
-
- Barber J. Crystal Structure of the Oxygen-Evolving Complex of Photosystem II. Inorg Chem. 2008;47:1700–1710. - PubMed
-
- Guskov A, Kern J, Gabdulkhakov A, Broser M, Zouni A, Saenger W. Cyanobacterial Photosystem II at 2.9-Å Resolution and the Role of Quinones, Lipids, Channels, and Chloride. Nature Struct & Mol Biol. 2009;16:334–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

