Key signalling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer. The Snail1-Twist1 conspiracy in malignant breast cancer progression
- PMID: 20594364
- PMCID: PMC2917026
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2585
Key signalling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer. The Snail1-Twist1 conspiracy in malignant breast cancer progression
Abstract
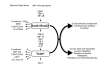
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women, and despite significant advances in diagnosing and treating it, metastatic spread of cancer cells results in a high mortality rate. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an embryonic program in which epithelial cells lose their characteristics and gain mesenchymal features. Therefore, EMT might play a very important role during malignant tumour progression. In this review we summarise recent advances in breast cancer research with a particular focus on the transcription factors Snail1 and Twist1. Besides discussing the role of EMT in normal mammary gland development, we describe regulatory mechanisms involving newly discovered upstream regulators and microRNAs, the association of EMT with breast cancer stem cells, and the involvement of the tumour microenvironment in breast cancer progression.
Figures
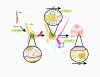
Similar articles
-
Temporal and spatial cooperation of Snail1 and Twist1 during epithelial-mesenchymal transition predicts for human breast cancer recurrence.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Dec;9(12):1644-57. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0371. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22006115 Free PMC article.
-
Twist1-mediated adriamycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition relates to multidrug resistance and invasive potential in breast cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 15;15(8):2657-65. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2372. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19336515
-
TGF-β-Id1 signaling opposes Twist1 and promotes metastatic colonization via a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition.Cell Rep. 2013 Dec 12;5(5):1228-42. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.11.014. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 24332369 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of EMT-inducing Transcription Factors (EMT-TFs) in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 23;6:28587. doi: 10.1038/srep28587. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27335258 Free PMC article.
-
AKT-ions with a TWIST between EMT and MET.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):62767-62777. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11232. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27623213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Down-regulation of CDH1 is associated with expression of SNAI1 in colorectal adenomas.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046665. Epub 2012 Sep 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029563 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the CXCR4-LASP1 Axis in the Stabilization of Snail1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 21;12(9):2372. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092372. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825729 Free PMC article.
-
Major Functional Transcriptome of an Inferred Center Regulator of an ER(-) Breast Cancer Model System.Cancer Inform. 2012;11:87-111. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S8633. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Cancer Inform. 2012. PMID: 22553414 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Suppresses Twist to Induce Apoptosis in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 22;10(10):e0141370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141370. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26491966 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulus-dependent differences in signalling regulate epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity and change the effects of drugs in breast cancer cell lines.Cell Commun Signal. 2015 May 15;13:26. doi: 10.1186/s12964-015-0106-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 25975820 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

