Early Experience Studying Cerebral Aneurysms with Rotational and Threedimensional Angiography and Review of CT and MR Angiography Literature
- PMID: 20594499
- PMCID: PMC3572494
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990200800407
Early Experience Studying Cerebral Aneurysms with Rotational and Threedimensional Angiography and Review of CT and MR Angiography Literature
Abstract
From september 2000 to september 2001, 32 consecutive patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms were examined with rotational and 3D reconstruction angiography using an Integris V5000 Philips Medical System: 39 aneurysms were detected. After a selective cerebral artery was catheterized with a 5F or 4F-catheter, 35 ml of contrast medium was intra-arterially administered at a rate of 4 ml/s and a 180 degrees rotational angiography was performed in eight seconds. This information was transferred to a computer (Silicon Graphics Octane) with software (Integris 3DRA, Philips Integris Systems) and a three-dimensional reconstruction was made. The information provided by Angio-3D was useful for evaluating the parent artery, aneurysmal sac, aneurysmal neck and arterial branches. It was also very useful in selecting the therapeutic method. For open surgery, this technique provides preoperative images that are useful for planning microsurgical approaches, especially in cases of large aneurysm showing complex surrounding arteries. For endovascular embolization, various anatomic characteristics of the aneurysm such as neck and sac size, shape, lobularity, parent artery and arterial branches adjacent to the aneurysmal neck must be demonstrated. This is very important to determine the best projection for embolization and to avoid multiple series. This is also essential in the choice of the first coil to create a good basket producing total occlusion. Microaneurysms are demonstrated well with this technique whereas this is difficult to do with conventional arteriography. The Angio-RM and Angio-CT literature show a lower sensitivity and specificity in comparasion with our experience with 3D IA-ROT-DSA. For this reason, we believe that 3D IA-ROTDSA is now the gold standard for patients presenting intracranial aneurysms.
Figures
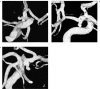







References
-
- Viñuela F, Duckwiler G, Mawad M. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg. 1997;86:475–482. - PubMed
-
- Nomura M, Kida S, et al. Pre-embolization study of ruptured cerebral aneurysms with helical TC. Interventional Neuroradilogy. 1999;5(suppl 1):219–223. - PubMed
-
- Murayama Y, Viñuela F, et al. Endovascular treatment of incidental cerebral aneurysms. Interventional Neuroradiology. 1999;5(suppl 1):79–81. - PubMed
-
- Rhoton AL. Microsurgical anatomy of saccular aneurysms. In: Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS, editors. Neurosurgery. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company; 1990. pp. 1330–1340.
-
- Waugh JR, Sacharias N. Arteriographic Complications in the DSA Era. Radiology. 1992;182:243–246. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

