Endovascular coil occlusion of intracranial aneurysms assisted by a novel self-expandable nitinol microstent (neuroform)
- PMID: 20594519
- PMCID: PMC3576604
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990200800202
Endovascular coil occlusion of intracranial aneurysms assisted by a novel self-expandable nitinol microstent (neuroform)
Abstract
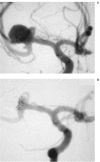
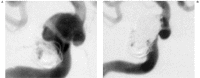
Endovascular treatment of wide neck intracranial aneurysms is technically difficult and leads to less favorable treatment results and long term outcome. We participated in a multicenter prospective study to evaluate the safety and performance of a new self-expandable nitinol micro stent (Neuroform) in stent assisted coil occlusion of wide neck intracranial aneurysms. Eighteen patients were enrolled in the study in a single center. The anatomy of the target aneurysm and the parent vessel, technical details of the procedure, device functionality, anatomic and clinical results were evaluated. All enrolled aneurysms were either wide necked or showed an unfavorable neck-to-fundus ratio. In 16 out of 18 patients the Neuroform device allowed stent assisted coil occlusion of the aneurysm. The occlusion rate was 95% in eight patients and 100% in eight patients. The two failures were both due to anatomic reasons. Flexibility of the stent, behavior during deployment and subsequent ability to retain coils within the aneurysmal sac were considered as good as or better than the properties of previous balloon expandable stents. No device-related adverse events were encountered. Procedure-related clinical complications occurred in seven patients but caused no severe permanent neurological deficit. The Neuroform neurovascular stenting system is a safe and effective adjunct for the stent-assisted coil occlusion of wide necked intracranial aneurysms. The major advantages of this device are its self-expanding property and very high flexibility which allows safe navigation, easy sizing, as well as accurate positioning of the stent while providing sufficient bridging of the aneurysm neck for subsequent coil placement.
Figures

References
-
- Lot G, Houdart E, et al. Combined management of intracranial aneurysms by surgical and endovascular treatment. Modalities and results from a series of 395 cases. Acta Neurochir. 1999;141:557–562. - PubMed
-
- Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg. 1997;86:475–482. - PubMed
-
- Assali AR, Sdringola S, et al. Endovascular repair of traumatic pseudoaneurysm by uncovered self-expandable stenting with or without transstent coiling of the aneurysm cavity. Cathet Cardiovasc Intervent. 2001;53:253–258. - PubMed
-
- Bai H, Masuda J, et al. Neointima formation after vascular stent implantation. Spatial and chronological distribution of smooth muscle cell proliferation and phenotypic modulation. Arterioscler Throm. 1994;14:1846–1853. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

