P2Y nucleotide receptors: promise of therapeutic applications
- PMID: 20594935
- PMCID: PMC2920619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.05.011
P2Y nucleotide receptors: promise of therapeutic applications
Abstract
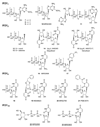
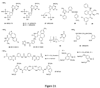
Extracellular nucleotides, such as ATP and UTP, have distinct signaling roles through a class of G-protein-coupled receptors, termed P2Y. The receptor ligands are typically charged molecules of low bioavailability and stability in vivo. Recent progress in the development of selective agonists and antagonists for P2Y receptors and study of knockout mice have led to new drug concepts based on these receptors. The rapidly accelerating progress in this field has already resulted in drug candidates for cystic fibrosis, dry eye disease and thrombosis. On the horizon are novel treatments for cardiovascular diseases, inflammatory diseases and neurodegeneration.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Idzko M, et al. Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat. Med. 2007;13:913–919. - PubMed
-
- Boeynaems JM, et al. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2005;31:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Lazarowski ER, et al. Mechanisms of release of nucleotides and integration of their action as P2X- and P2Y-receptor activating molecules. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003;64:785–795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

