Acute oxidative stress and systemic Nrf2 activation by the ketogenic diet
- PMID: 20594978
- PMCID: PMC3102314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.05.030
Acute oxidative stress and systemic Nrf2 activation by the ketogenic diet
Abstract
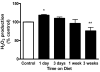
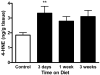
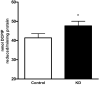
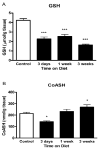
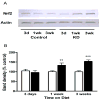
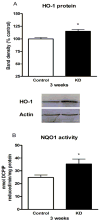
The mechanisms underlying the efficacy of the ketogenic diet (KD) remain unknown. Recently, we showed that the KD increased glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis. Since the NF E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) transcription factor is a primary responder to cellular stress and can upregulate GSH biosynthesis, we asked whether the KD activates the Nrf2 pathway. Here we report that rats consuming a KD show acute production of H(2)O(2) from hippocampal mitochondria, which decreases below control levels by 3 weeks, suggestive of an adaptive response. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), an electrophilic lipid peroxidation end product known to activate the Nrf2 detoxification pathway, was also acutely increased by the KD. Nrf2 nuclear accumulation was evident in both the hippocampus and liver, and the Nrf2 target, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1), exhibited increased activity in both the hippocampus and liver after 3 weeks. We also found chronic depletion of liver tissue GSH, while liver mitochondrial antioxidant capacity was preserved. These data suggest that the KD initially produces mild oxidative and electrophilic stress, which may systemically activate the Nrf2 pathway via redox signaling, leading to chronic cellular adaptation, induction of protective proteins, and improvement of the mitochondrial redox state.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Appleton DB, DeVivo DC. An animal model for the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 1974;15:211–227. - PubMed
-
- Bough KJ, Wetherington J, Hassel B, Pare JF, Gawryluk JW, Greene JG, Shaw R, Smith Y, Geiger JD, Dingledine RJ. Mitochondrial biogenesis in the anticonvulsant mechanism of the ketogenic diet. Ann Neurol. 2006;60:223–235. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZH, Saito Y, Yoshida Y, Sekine A, Noguchi N, Niki E. 4-Hydroxynonenal induces adaptive response and enhances PC12 cell tolerance primarily through induction of thioredoxin reductase 1 via activation of Nrf2. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:41921–41927. - PubMed
-
- Dehn DL, Siegel D, Zafar KS, Reigan P, Swann E, Moody CJ, Ross D. 5-Methoxy-1,2-dimethyl-3-[(4-nitrophenoxy)methyl]indole-4,7-dione, a mechanism-based inhibitor of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1, exhibits activity against human pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:1702–1709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

