Host-derived interleukin-5 promotes adenocarcinoma-induced malignant pleural effusion
- PMID: 20595227
- PMCID: PMC3001265
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201001-0001OC
Host-derived interleukin-5 promotes adenocarcinoma-induced malignant pleural effusion
Abstract
Rationale: IL-5 is a T helper 2 cytokine important in the trafficking and survival of eosinophils. Because eosinophils can be found in malignant pleural effusions (MPE) from mice and humans, we asked whether IL-5 is involved in the pathogenesis of MPE.
Objectives: To determine the role of IL-5 in MPE formation.
Methods: The effects of IL-5 on experimental MPE induced in C57BL/6 mice by intrapleural injection of syngeneic lung (Lewis lung cancer [LLC]) or colon (MC38) adenocarcinoma cells were determined using wild-type (il5(+/+)) and IL-5-deficient (il5⁻(/)⁻) mice, exogenous administration of recombinant mouse (rm) IL-5, and in vivo antibody-mediated neutralization of endogenous IL-5. The direct effects of rmIL-5 on LLC cell proliferation and gene expression in vitro were determined by substrate reduction and microarray.
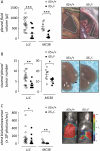
Measurements and main results: Eosinophils and IL-5 were present in human and mouse MPE, but the cytokine was not detected in mouse (LLC) or human (A549) lung and mouse colon (MC38) adenocarcinoma-conditioned medium, suggesting production by host cells in MPE. Compared with il5(+/+) mice, il5⁻(/)⁻ mice showed markedly diminished MPE formation in response to both LLC and MC38 cells. Exogenous IL-5 promoted MPE formation in il5(+/+) and il5⁻(/)⁻ mice, whereas anti-IL-5 antibody treatment limited experimental MPE in il5(+/+) mice. Exogenous IL-5 had no effects on LLC cell proliferation and gene expression; however, IL-5 was found to be responsible for recruitment of eosinophils and tumor-promoting myeloid suppressor cells to MPE in vivo.
Conclusions: Host-derived IL-5 promotes experimental MPE and may be involved in the pathogenesis of human MPE.
Figures


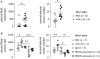


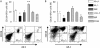
Similar articles
-
Beneficial impact of CCL2 and CCL12 neutralization on experimental malignant pleural effusion.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 14;8(8):e71207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071207. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967166 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 inhibits development of malignant pleural effusion via interleukin-9-dependent mechanism.Sci China Life Sci. 2016 Dec;59(12):1297-1304. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-0097-y. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Sci China Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27535421
-
Specific effects of bortezomib against experimental malignant pleural effusion: a preclinical study.Mol Cancer. 2010 Mar 10;9:56. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-56. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20219102 Free PMC article.
-
Closing faucets: the role of anti-angiogenic therapies in malignant pleural diseases.Clin Transl Oncol. 2016 Aug;18(8):760-8. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1464-y. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Clin Transl Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26680633 Review.
-
Malignant pleural effusion: tumor-host interactions unleashed.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Sep 15;186(6):487-92. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201203-0465PP. Epub 2012 May 31. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22652027 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Malignant pleural effusion: from bench to bedside.Eur Respir Rev. 2016 Jun;25(140):189-98. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0019-2016. Eur Respir Rev. 2016. PMID: 27246596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells interact with tumors in terms of myelopoiesis, tumorigenesis and immunosuppression: thick as thieves.J Cancer. 2013;4(1):3-11. doi: 10.7150/jca.5047. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23386900 Free PMC article.
-
Pleural involvement in lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2015 Jun;7(6):1021-30. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.04.23. J Thorac Dis. 2015. PMID: 26150915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial impact of CCL2 and CCL12 neutralization on experimental malignant pleural effusion.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 14;8(8):e71207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071207. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967166 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-5-producing malignant pleural mesothelioma with eosinophilic pleural effusion.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Oct;11(10):3043-3046. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13652. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32894005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Light RW. Clinical practice: pleural effusion. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1971–1977. - PubMed
-
- Antony VB, Loddenkemper R, Astoul P, Boutin C, Goldstraw P, Hott J, Rodriguez Panadero F, Sahn SA. Management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:1987–2001. - PubMed
-
- Light RW, Lee YCG. Textbook of pleural diseases, 2nd ed. London: Hodder and Arnold; 2008.
-
- Sugiura S, Ando Y, Minami H, Ando M, Sakai S, Shimokata K. Prognostic value of pleural effusion in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:47–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

