Host-derived interleukin-5 promotes adenocarcinoma-induced malignant pleural effusion
- PMID: 20595227
- PMCID: PMC3001265
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201001-0001OC
Host-derived interleukin-5 promotes adenocarcinoma-induced malignant pleural effusion
Abstract
Rationale: IL-5 is a T helper 2 cytokine important in the trafficking and survival of eosinophils. Because eosinophils can be found in malignant pleural effusions (MPE) from mice and humans, we asked whether IL-5 is involved in the pathogenesis of MPE.
Objectives: To determine the role of IL-5 in MPE formation.
Methods: The effects of IL-5 on experimental MPE induced in C57BL/6 mice by intrapleural injection of syngeneic lung (Lewis lung cancer [LLC]) or colon (MC38) adenocarcinoma cells were determined using wild-type (il5(+/+)) and IL-5-deficient (il5⁻(/)⁻) mice, exogenous administration of recombinant mouse (rm) IL-5, and in vivo antibody-mediated neutralization of endogenous IL-5. The direct effects of rmIL-5 on LLC cell proliferation and gene expression in vitro were determined by substrate reduction and microarray.
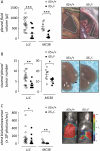
Measurements and main results: Eosinophils and IL-5 were present in human and mouse MPE, but the cytokine was not detected in mouse (LLC) or human (A549) lung and mouse colon (MC38) adenocarcinoma-conditioned medium, suggesting production by host cells in MPE. Compared with il5(+/+) mice, il5⁻(/)⁻ mice showed markedly diminished MPE formation in response to both LLC and MC38 cells. Exogenous IL-5 promoted MPE formation in il5(+/+) and il5⁻(/)⁻ mice, whereas anti-IL-5 antibody treatment limited experimental MPE in il5(+/+) mice. Exogenous IL-5 had no effects on LLC cell proliferation and gene expression; however, IL-5 was found to be responsible for recruitment of eosinophils and tumor-promoting myeloid suppressor cells to MPE in vivo.
Conclusions: Host-derived IL-5 promotes experimental MPE and may be involved in the pathogenesis of human MPE.
Figures


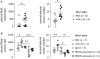


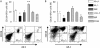
References
-
- Light RW. Clinical practice: pleural effusion. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1971–1977. - PubMed
-
- Antony VB, Loddenkemper R, Astoul P, Boutin C, Goldstraw P, Hott J, Rodriguez Panadero F, Sahn SA. Management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:1987–2001. - PubMed
-
- Light RW, Lee YCG. Textbook of pleural diseases, 2nd ed. London: Hodder and Arnold; 2008.
-
- Sugiura S, Ando Y, Minami H, Ando M, Sakai S, Shimokata K. Prognostic value of pleural effusion in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:47–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

