Sphenoid masses in children: radiologic differential diagnosis with pathologic correlation
- PMID: 20595365
- PMCID: PMC7965862
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2144
Sphenoid masses in children: radiologic differential diagnosis with pathologic correlation
Abstract
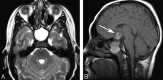
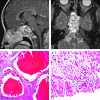
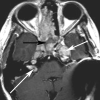
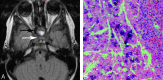
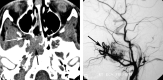
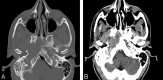
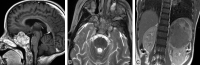
Childhood central skull base masses are rare, often difficult to diagnose, and have overlapping imaging findings. In this review, we provide an overview of the epidemiology, clinical findings, and management of pediatric sphenoid bone and sphenoid sinus masses with an emphasis on imaging findings that may help to differentiate lesions. Radiologic-pathologic correlation is provided. Finally, an imaging-based algorithm is presented as a guide to help radiologists narrow their differential diagnoses. Some of the entities discussed are virtually unique to the pediatric population; others occur rarely in this age group but should be considered in the appropriate clinical setting. Entities included in the discussion are grouped into 2 categories: those that cause nonaggressive osseous remodeling and those that are more commonly associated with aggressive bone changes. Mucocele, aneurysmal bone cyst, giant cell lesions, meningioma, and fibrous dysplasia tend to remodel bone, while entities such as chordoma, craniopharyngioma, rhabdomyosarcoma, sinonasal carcinoma, and neuroblastoma may cause more aggressive local bone changes.
Figures






References
-
- Levine H. The sphenoid sinus, the neglected nasal sinus. Arch Otolaryngol 1978;104:585–87 - PubMed
-
- Grossman RI, Yousem DM. Neuroradiology: The Requisites. St. Louis:Mosby-Year Book Inc;1994
-
- Alvarez RJ, Liu NJ, Isaacson G. Pediatric ethmoid mucoceles in cystic fibrosis: long-term follow-up of reported cases. Ear Nose Throat J 1997;76:538–39,543–46 - PubMed
-
- Bailey BJ, Johnson JT, Newlands SD, eds. Head & Neck Surgery: Otolaryngology. 4th ed. Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006
-
- Stankiewicz JA. Sphenoid sinus mucocele. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1989;115:735–40 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
