CASE REPORT Superficial Spreading Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Face: A Surgical Challenge
- PMID: 20596236
- PMCID: PMC2890390
CASE REPORT Superficial Spreading Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Face: A Surgical Challenge
Abstract
Objective: We present the case of a white man with a facial nodule suspicious for basal cell carcinoma.
Methods: Biopsy revealed clusters of basaloid tumor cells with peripheral palisading, consistent with a superficial spreading variant of basal cell carcinoma.
Results: The patient was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery, with clear margins achieved after the second stage of excision. However, since it was a superficial spreading basal cell carcinoma, this was followed by topical imiquimod treatment.
Conclusion: Topical chemotherapy with imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil may be valuable alternatives or adjuncts, given the increased likelihood of recurrence after surgical excision of superficial spreading basal cell carcinoma. Mohs surgery is of limited value in the management of superficial spreading basal cell carcinoma because it characteristically shows areas of uninvolved skin between tumor nests.
Figures

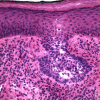
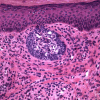
References
-
- Raasch BA, Buettner PG, Garbe C. Basal cell carcinoma: histological classification and body-site distribution. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:401–7. - PubMed
-
- Buljan M, Bulat V, Situm M, Mihic LL, Stanic-Duktaj S. Variations in clinical presentation of basal cell carcinoma. Acta Clin Croat. 2008;47:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Chen CC, Chen CL. Clinical and histopathologic findings of superficial basal cell carcinoma: a comparison with other basal cell carcinoma subtypes. J Chin Med Assoc. 2006;69:364–71. - PubMed
-
- Lovatt TJ, Lear JT, Bastrilles J, et al. Associations between ultraviolet radiation, basal cell carcinoma site and histology, host characteristics, and rate of development of further tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:468–73. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy C, Bajdik CD, Willemze R, De Gruijl FR, Bouwes Bavinck JN. The influence of painful sunburns and lifetime sun exposure on the risk of actinic keratoses, seborrheic warts, melanocytic nevi, atypical nevi, and skin cancer. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;120:1087–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
