Selection of housekeeping genes for use in quantitative reverse transcription PCR assays on the murine cornea
- PMID: 20596249
- PMCID: PMC2893048
Selection of housekeeping genes for use in quantitative reverse transcription PCR assays on the murine cornea
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the suitability of common housekeeping genes (HKGs) for use in quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) assays of the cornea in various murine disease models.
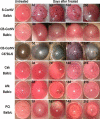
Methods: CORNEAL DISEASE MODELS STUDIED WERE: 1) corneal neovascularization (CorNV) induced by suture or chemical burn, 2) corneal infection with Candida albicans or Aspergillus fumigatus by intrastromal injection of live spores, and 3) perforating corneal injury (PCI) in Balb/c mice or C57BL/6 mice. Expression of 8 HKGs (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [GAPDH], beta-actin [ACTB], lactate dehydrogenase A [LDHA], ribosomal protein L5 [RPL5], ubiquitin C [UBC], peptidylprolyl isomerase A [PPIA], TATA-box binding protein [TBP1], and hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase [HPRT1]) in the cornea were measured at various time points by microarray hybridization or qRT-PCR and the data analyzed using geNorm and NormFinder.
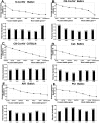
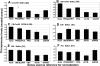
Results: Microarray results showed that under the CorNV condition the expression stability of the 8 HKGs decreased in order of PPIA>RPL5>HPRT1>ACTB>UBC>TBP1>GAPDH>LDHA. qRT-PCR analyses demonstrated that expression of none of the 8 HKGs remained stable under all conditions, while GAPDH and ACTB were among the least stably expressed markers under most conditions. Both geNorm and NormFinder analyses proposed best HKGs or HKG combinations that differ between the various models. NormFinder proposed PPIA as best HKG for three CorNV models and PCI model, as well as UBC for two fungal keratitis models. geNorm analysis demonstrated that a similar model in different mice strains or caused by different stimuli may require different HKGs or HKG pairs for the best normalization. Namely, geNorm proposed PPIA and HRPT1 and PPIA and RPL5 pairs for chemical burn-induced CorNV in Balb/c and C57BL/6 mice, respectively, while UBC and HPRT1 and UBC and LDHA were best for Candida and Aspergillus induced keratitis in Balb/c mice, respectively.
Conclusions: When qRT-PCR is designed for studies of gene expression in murine cornea, preselection of situation-specific reference genes is recommended. In the absence of knowledge about situation-specific HKGs, PPIA and UBC, either alone or in combination with HPRT1 or RPL5, can be employed.
Figures
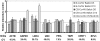

Similar articles
-
Validation of endogenous control genes for gene expression studies on human ocular surface epithelium.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022301. Epub 2011 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21857920 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of genome-wide gene expression in suture- and alkali burn-induced murine corneal neovascularization.Mol Vis. 2011;17:2386-99. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21921991 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of suitable reference genes for gene expression studies using quantitative polymerase chain reaction in lung cancer in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2015 May;11(5):3767-73. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3159. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25573171
-
Identification of valid reference housekeeping genes for gene expression analysis in tumor neovascularization studies.Clin Transl Oncol. 2013 Mar;15(3):211-8. doi: 10.1007/s12094-012-0904-1. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22855186
-
DNA methylation modification: Dawn of research on cornea-related diseases.Life Sci. 2025 Sep 1;376:123757. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123757. Epub 2025 May 22. Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40412607 Review.
Cited by
-
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into cells with corneal keratocyte phenotype.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056831. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437251 Free PMC article.
-
Lung-Targeted Itraconazole Delivery Using PVA-Based Nano-in-Microparticles for Improved Treatment of Pulmonary Aspergillosis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 8;20:4357-4380. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S511099. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40230542 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR studies in Candida glabrata following azole treatment.BMC Mol Biol. 2012 Jun 29;13:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-13-22. BMC Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22747760 Free PMC article.
-
Reference genes for measuring mRNA expression.Theory Biosci. 2012 Dec;131(4):215-23. doi: 10.1007/s12064-012-0152-5. Epub 2012 May 17. Theory Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22588998 Review.
-
Evaluation of critical design parameters for RT-qPCR-based analysis of multiple dUTPase isoform genes in mice.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Jun;9(6):1153-1170. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12654. Epub 2019 May 29. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 31077566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thellin O, Zorzi W, Lakaye B, De Borman B, Coumans B, Hennen G, Grisar T, Igout A, Heinen E. Housekeeping genes as internal standards: use and limits. J Biotechnol. 1999;75:291–5. - PubMed
-
- Barber RD, Harmer DW, Coleman RA, Clark BJ. GAPDH as a housekeeping gene: analysis of GAPDH mRNA expression in a panel of 72 human tissues. Physiol Genomics. 2005;21:389–95. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, Higgins PJ, Crawford DR. Control selection for RNA quantitation. Biotechniques. 2000;29:332–7. - PubMed
-
- Selvey S, Thompson EW, Matthaei K, Lea RA, Irving MG, Griffiths LR. Beta-actin–an unsuitable internal control for RT-PCR. Mol Cell Probes. 2001;15:307–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
