Tin oxide nanorod array-based electrochemical hydrogen peroxide biosensor
- PMID: 20596358
- PMCID: PMC2894215
- DOI: 10.1007/s11671-010-9622-1
Tin oxide nanorod array-based electrochemical hydrogen peroxide biosensor
Abstract
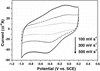
SnO2 nanorod array grown directly on alloy substrate has been employed as the working electrode of H2O2 biosensor. Single-crystalline SnO2 nanorods provide not only low isoelectric point and enough void spaces for facile horseradish peroxidase (HRP) immobilization but also numerous conductive channels for electron transport to and from current collector; thus, leading to direct electrochemistry of HRP. The nanorod array-based biosensor demonstrates high H2O2 sensing performance in terms of excellent sensitivity (379 μA mM-1 cm-2), low detection limit (0.2 μM) and high selectivity with the apparent Michaelis-Menten constant estimated to be as small as 33.9 μM. Our work further demonstrates the advantages of ordered array architecture in electrochemical device application and sheds light on the construction of other high-performance enzymatic biosensors.
Keywords: Biosensor; Nanorod array; Nanostructure; SnO2.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

