Fabrication of Highly Ordered Polymeric Nanodot and Nanowire Arrays Templated by Supramolecular Assembly Block Copolymer Nanoporous Thin Films
- PMID: 20596454
- PMCID: PMC2893920
- DOI: 10.1007/s11671-009-9263-4
Fabrication of Highly Ordered Polymeric Nanodot and Nanowire Arrays Templated by Supramolecular Assembly Block Copolymer Nanoporous Thin Films
Abstract
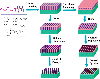
Realizing the vast technological potential of patternable block copolymers requires both the precise controlling of the orientation and long-range ordering, which is still a challenging topic so far. Recently, we have demonstrated that ordered nanoporous thin film can be fabricated from a simple supramolecular assembly approach. Here we will extend this approach and provide a general route to fabricate large areas of highly ordered polymeric nanodot and nanowire arrays. We revealed that under a mixture solvent annealing atmosphere, a near-defect-free nanoporous thin film over large areas can be achieved. Under the direction of interpolymer hydrogen bonding and capillary action of nanopores, this ordered porous nanotemplate can be properly filled with phenolic resin precursor, followed by curation and pyrolysis at middle temperature to remove the nanotemplate, a perfect ordered polymer nanodot arrays replication was obtained. The orientation of the supramolecular assembly thin films can be readily re-aligned parallel to the substrate upon exposure to chloroform vapor, so this facile nanotemplate replica method can be further extend to generate large areas of polymeric nanowire arrays. Thus, we achieved a successful sub-30 nm patterns nanotemplates transfer methodology for fabricating polymeric nanopattern arrays with highly ordered structure and tunable morphologies.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

