Verteporfin photodynamic therapy combined with intravitreal triamcinolone for choroidal neovascularization due to angioid streaks
- PMID: 20596507
- PMCID: PMC2893762
- DOI: 10.2147/opth.s10649
Verteporfin photodynamic therapy combined with intravitreal triamcinolone for choroidal neovascularization due to angioid streaks
Abstract
Purpose: To report the visual outcome of photodynamic therapy (PDT) combined with intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA) for choroidal neovascularization (CNV) secondary to angioid streaks (AS).
Methods: Five eyes of five consecutive patients (mean age 45 +/- 10 years) with CNV secondary to AS were treated by combination of PDT and IVTA. TA (4 mg/0.1 mL) was injected 7 days before PDT.
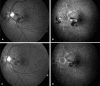
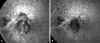
Results: All patients completed the 12-month follow-up. CNV was subfoveal in three cases and extrafoveal in two. Median best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 0.3 LogMAR (70 letters) at baseline (range 1.3-0.1), and 0.5 LogMAR (60 letters) at the final examination (range 1.0-0.1). At 12 months, one patient had severe visual deterioration, with a loss of seven lines of VA; Two patients lost up to three lines. One patient had no change in BCVA and the fifth gained nine lines of VA. Two patients received one further combination of PDT and IVTA after the first combination treatment. All eyes showed the CNV closure at the 12-month follow-up visit.
Conclusions: Combination of PDT and IVTA may reduce the need for retreatment and could be potentially useful for preserving vision in some patients with CNV due to AS.
Keywords: ocular corticosteroids.
Figures

References
-
- Mansour AM, Shields JA, Annesley WH, Jr, et al. Macular degeneration in angioid streaks. Ophthalmologica. 1988;197:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Clarkson JG, Altman RD. Angioid streaks. Surv Ophthalmol. 1982;26:235–246. - PubMed
-
- Singerman LJ, Hatem G. Laser treatment of choroidal neovascular membranes in angioid streaks. Retina. 1981;1:75–83. - PubMed
-
- Pece A, Avanza P, Galli L, Brancato R. Laser photocoagulation of choroidal neovascularization in angioid streaks. Retina. 1997;17:12–16. - PubMed
-
- Menchini U, Virgili G, Introini U, et al. Outcome of choroidal neovascularization in angioid streaks after photodynamic therapy. Retina. 2004;24:763–771. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

