MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 is required for mouse meiotic spindle assembly and kinetochore-microtubule attachment
- PMID: 20596525
- PMCID: PMC2893158
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011247
MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 is required for mouse meiotic spindle assembly and kinetochore-microtubule attachment
Abstract
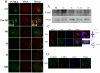
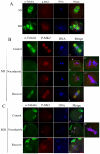
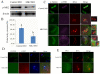
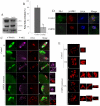
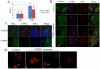
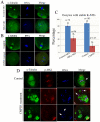
MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2), a direct substrate of p38 MAPK, plays key roles in multiple physiological functions in mitosis. Here, we show for the first time the unique distribution pattern of MK2 in meiosis. Phospho-MK2 was localized on bipolar spindle minus ends and along the interstitial axes of homologous chromosomes extending over centromere regions and arm regions at metaphase of first meiosis (MI stage) in mouse oocytes. At metaphase of second meiosis (MII stage), p-MK2 was localized on the bipolar spindle minus ends and at the inner centromere region of sister chromatids as dots. Knockdown or inhibition of MK2 resulted in spindle defects. Spindles were surrounded by irregular nondisjunction chromosomes, which were arranged in an amphitelic or syntelic/monotelic manner, or chromosomes detached from the spindles. Kinetochore-microtubule attachments were impaired in MK2-deficient oocytes because spindle microtubules became unstable in response to cold treatment. In addition, homologous chromosome segregation and meiosis progression were inhibited in these oocytes. Our data suggest that MK2 may be essential for functional meiotic bipolar spindle formation, chromosome segregation and proper kinetochore-microtubule attachments.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Nasmyth K. Disseminating the genome: joining, resolving, and separating sister chromatids during mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 2001;35:673–745. - PubMed
-
- Marston AL, Amon A. Meiosis: cell-cycle controls shuffle and deal. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:983–997. - PubMed
-
- Kline-Smith SL, Walczak CE. Mitotic spindle assembly and chromosome segregation: refocusing on microtubule dynamics. Mol Cell. 2004;15:317–327. - PubMed
-
- Tong C, Fan HY, Lian L, Li SW, Chen DY, et al. Polo-like kinase-1 is a pivotal regulator of microtubule assembly during mouse oocyte meiotic maturation, fertilization, and early embryonic mitosis. Biol Reprod. 2002;67:546–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

