CXCR2 signaling protects oligodendrocytes and restricts demyelination in a mouse model of viral-induced demyelination
- PMID: 20596532
- PMCID: PMC2893165
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011340
CXCR2 signaling protects oligodendrocytes and restricts demyelination in a mouse model of viral-induced demyelination
Abstract
Background: The functional role of ELR-positive CXC chemokines during viral-induced demyelination was assessed. Inoculation of the neuroattenuated JHM strain of mouse hepatitis virus (JHMV) into the CNS of susceptible mice results in an acute encephalomyelitis that evolves into a chronic demyelinating disease, modeling white matter pathology observed in the human demyelinating disease Multiple Sclerosis.
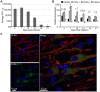
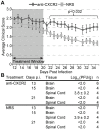
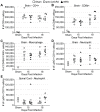
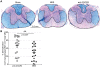
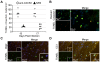
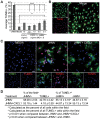
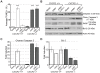
Methodology/principal findings: JHMV infection induced the rapid and sustained expression of transcripts specific for the ELR+ chemokine ligands CXCL1 and CXCL2, as well as their binding receptor CXCR2, which was enriched within the spinal cord during chronic infection. Inhibiting CXCR2 signaling with neutralizing antiserum significantly (p<0.03) delayed clinical recovery. Moreover, CXCR2 neutralization was associated with an increase in the severity of demyelination that was independent of viral recrudescence or modulation of neuroinflammation. Rather, blocking CXCR2 was associated with increased numbers of apoptotic cells primarily within white matter tracts, suggesting that oligodendrocytes were affected. JHMV infection of enriched oligodendrocyte progenitor cell (OPC) cultures revealed that apoptosis was associated with elevated expression of cleaved caspase 3 and muted Bcl-2 expression. Inclusion of CXCL1 within JHMV infected cultures restricted caspase 3 cleavage and increased Bcl-2 expression that was associated with a significant (p<0.001) decrease in apoptosis. CXCR2 deficient oligodendrocytes were refractory to CXCL1 mediated protection from JHMV-induced apoptosis, readily activating caspase 3 and down regulating Bcl-2.
Conclusion/significance: These findings highlight a previously unappreciated role for CXCR2 signaling in protecting oligodendrocyte lineage cells from apoptosis during inflammatory demyelination initiated by viral infection of the CNS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
CXCR2 signaling protects oligodendrocyte progenitor cells from IFN-γ/CXCL10-mediated apoptosis.Glia. 2011 Oct;59(10):1518-28. doi: 10.1002/glia.21195. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21656856 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted CXCR2 Signaling in Oligodendroglia Lineage Cells Enhances Myelin Repair in a Viral Model of Multiple Sclerosis.J Virol. 2019 Aug 28;93(18):e00240-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00240-19. Print 2019 Sep 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31243125 Free PMC article.
-
A protective role for ELR+ chemokines during acute viral encephalomyelitis.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Nov;5(11):e1000648. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000648. Epub 2009 Nov 6. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19893623 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR2 Signaling and Remyelination in Preclinical Models of Demyelination.DNA Cell Biol. 2020 Jan;39(1):3-7. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.5182. Epub 2019 Dec 17. DNA Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31851535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemokine receptor CXCR2 and coronavirus-induced neurologic disease.Virology. 2013 Jan 5;435(1):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.08.049. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23217621 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulated Chemokine Signaling in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease: A Potential Therapeutic Target.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(13):1535-44. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666151209120516. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26648071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JCV agnoprotein-induced reduction in CXCL5/LIX secretion by oligodendrocytes is associated with activation of apoptotic signaling in neurons.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Aug;227(8):3119-27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.23065. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22034072 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR2 signaling and host defense following coronavirus-induced encephalomyelitis.Future Virol. 2012 Apr;7(4):349-359. doi: 10.2217/fvl.12.23. Future Virol. 2012. PMID: 22582084 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Chemokines in the Pathogenesis of HTLV-1.Front Microbiol. 2020 Mar 13;11:421. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00421. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32231656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCR2 signaling protects oligodendrocyte progenitor cells from IFN-γ/CXCL10-mediated apoptosis.Glia. 2011 Oct;59(10):1518-28. doi: 10.1002/glia.21195. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21656856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Florio T, Schettini G. Chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2001;22:147–184. - PubMed
-
- Ubogu EE, Cossoy MB, Ransohoff RM. The expression and function of chemokines involved in CNS inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:48–55. - PubMed
-
- Liu MT, Keirstead HS, Lane TE. Neutralization of the chemokine CXCL10 reduces inflammatory cell invasion and demyelination and improves neurological function in a viral model of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 2001;167:4091–4097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

