Preparation and Characterization of Cationic PLA-PEG Nanoparticles for Delivery of Plasmid DNA
- PMID: 20596550
- PMCID: PMC2893611
- DOI: 10.1007/s11671-009-9345-3
Preparation and Characterization of Cationic PLA-PEG Nanoparticles for Delivery of Plasmid DNA
Abstract
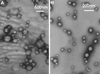
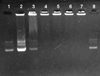
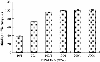
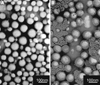
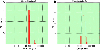
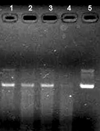
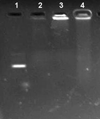
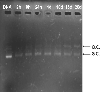
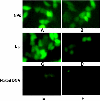
The purpose of the present work was to formulate and evaluate cationic poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) (PLA-PEG) nanoparticles as novel non-viral gene delivery nano-device. Cationic PLA-PEG nanoparticles were prepared by nanoprecipitation method. The gene loaded nanoparticles were obtained by incubating the report gene pEGFP with cationic PLA-PEG nanoparticles. The physicochemical properties (e.g., morphology, particle size, surface charge, DNA binding efficiency) and biological properties (e.g., integrity of the released DNA, protection from nuclease degradation, plasma stability, in vitro cytotoxicity, and in vitro transfection ability in Hela cells) of the gene loaded PLA-PEG nanoparticles were evaluated, respectively. The obtained cationic PLA-PEG nanoparticles and gene loaded nanoparticles were both spherical in shape with average particle size of 89.7 and 128.9 nm, polydispersity index of 0.185 and 0.161, zeta potentials of +28.9 and +16.8 mV, respectively. The obtained cationic PLA-PEG nanoparticles with high binding efficiency (>95%) could protect the loaded DNA from the degradation by nuclease and plasma. The nanoparticles displayed sustained-release properties in vitro and the released DNA maintained its structural and functional integrity. It also showed lower cytotoxicity than Lipofectamine 2000 and could successfully transfect gene into Hela cells even in presence of serum. It could be concluded that the established gene loaded cationic PLA-PEG nanoparticles with excellent properties were promising non-viral nano-device, which had potential to make cancer gene therapy achievable.
Figures

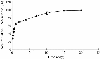
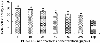
Similar articles
-
Preparation and Characterization of PLA-PEG-PLA/PEI/DNA Nanoparticles for Improvement of Transfection Efficiency and Controlled Release of DNA in Gene Delivery Systems.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Winter;18(1):125-141. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 31089350 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable tri-block copolymer poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(l-lysine)(PLA-PEG-PLL) as a non-viral vector to enhance gene transfection.Int J Mol Sci. 2011 Feb 23;12(2):1371-88. doi: 10.3390/ijms12021371. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21541064 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, characterization, and in vitro evaluation of docetaxel-loaded poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2010 Dec;6(6):675-82. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2010.1160. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2010. PMID: 21361132
-
Preparation, characterization, cytotoxicity and transfection efficiency of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) and poly(DL-lactic acid) cationic nanoparticles for controlled delivery of plasmid DNA.Int J Pharm. 2007 Oct 1;343(1-2):247-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.05.023. Epub 2007 May 18. Int J Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17611054 Free PMC article.
-
Pegylated poly(lactide) and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: preparation, properties and possible applications in drug delivery.Curr Drug Deliv. 2004 Oct;1(4):321-33. doi: 10.2174/1567201043334605. Curr Drug Deliv. 2004. PMID: 16305394 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides to Overcome the Limitations of Current Anticancer and Antimicrobial Nanotherapies.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 10;14(6):1235. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061235. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Characterization of PLA-PEG-PLA/PEI/DNA Nanoparticles for Improvement of Transfection Efficiency and Controlled Release of DNA in Gene Delivery Systems.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Winter;18(1):125-141. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 31089350 Free PMC article.
-
The Art of PEGylation: From Simple Polymer to Sophisticated Drug Delivery System.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 27;26(7):3102. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073102. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tween® Preserves Enzyme Activity and Stability in PLGA Nanoparticles.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Nov 3;11(11):2946. doi: 10.3390/nano11112946. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835710 Free PMC article.
-
Non-viral therapeutic approaches to ocular diseases: An overview and future directions.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 10;219:471-487. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26439665 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

