Aerobic training reverses high-fat diet-induced pro-inflammatory signalling in rat skeletal muscle
- PMID: 20596724
- PMCID: PMC5054743
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-010-1559-7
Aerobic training reverses high-fat diet-induced pro-inflammatory signalling in rat skeletal muscle
Abstract
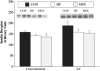
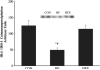
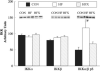
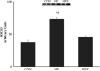
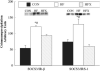
High-fat feeding activates components of the pro-inflammatory pathway and increases co-immunoprecipitation of suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS)-3 with both the insulin receptor (IR)-β subunit and IRS-1, which together contribute to keeping PI-3 kinase from being fully activated. However, whether aerobic training reverses these impairments is unknown. Sprague-Dawley rats were fed a chow (CON, n = 8) or saturated high-fat (n = 16) diets for 4 weeks. High-fat-fed rats were then allocated (n = 8/group) to either sedentary (HF) or aerobic exercise training (HFX) for an additional 4 weeks after which all animals underwent hind limb perfusions. Insulin-stimulated red quadriceps 3-O-methylglucose transport rates and PI-3 kinase activity were greater (p < 0.05) in CON and HFX compared to HF. IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation was increased (p < 0.05) and IRS-1 serine 307 phosphorylation was decreased (p < 0.05) in HFX compared to HF. IR-β subunit co-immunoprecipitation with IRS-1 was increased in HFX compared to HF. SOCS-3 co-immunoprecipitation with both the IR-β subunit and IRS-1 was decreased (p < 0.05) in HFX compared to HF. IKKα/β serine phosphorylation, and IκBα serine phosphorylation were decreased (p < 0.05) while IκBα protein concentration was increased in HFX compared to HF. By decreasing the association of SOCS-3 with both the IR-β subunit and IRS-1 the interaction between IRS-1 and the IR-β subunit was normalized in the HFX, and may have contributed to skeletal muscle PI-3 kinase being fully activated by insulin. Additionally, the reduction in IKKα/β serine phosphorylation in HFX may have contributed to decreasing IRS-1 serine phosphorylation, and in turn, promoted the normalization of insulin-stimulated activation of PI-3 kinase.
Figures



References
-
- Bhatt BA, Dube JJ, Dedousis N, Reider JA, O'Doherty RM. Diet-induced obesity and acute hyperlipidemia reduce IκBα levels in rat skeletal muscle in a fiber-type dependent manner. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006;290:R233–R240. - PubMed
-
- Boden G, She P, Mozzoli M, Cheung P, Gumireddy K, Reddy P, Xiang X, Luo Z, Ruderman N. Free fatty acids produce insulin resistance and activate the proinflammatory nuclear factor-kB pathway in rat liver. Diabetes. 2005;54:3458–3465. - PubMed
-
- Borst SE, Conover CF. High-fat diet induces increased tissue expression of TNF-α. Life Sci. 2005;77:2156–2165. - PubMed
-
- DiDonato JA, Hayakawa M, Rothwarf DM, Zandi E, Karin M. A cytokine-responsive IkappaB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Nature. 1997;388:548–554. - PubMed
-
- Emanuelli B, Peraldi P, Filloux C, Sawka-Verhelle D, Hilton D, Van Obberghen E. SOCS-3 is an insulin-induced negative regulator of insulin signaling. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:15985–15991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

