Mucoepidermoid carcinoma arising in a background of sialadenoma papilliferum: a case report
- PMID: 20596992
- PMCID: PMC2807533
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-009-0106-5
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma arising in a background of sialadenoma papilliferum: a case report
Abstract
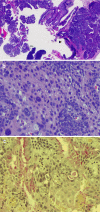
Sialadenoma papilliferum is a rare tumor, primarily of minor salivary gland origin, first described by Abrams and Finck (Cancer 24:1057-63, 1969). It is both an exophytic and endophytic papillary lesion histologically resembling syringocystadenoma papilliferum of sweat gland. The tumor is considered benign although rare recurrent cases have been reported. Three cases of malignant transformation of sialadenoma papilliferum have been described in the literature. We report a high grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma arising in a background of sialadenoma papilliferum, at the base of the tongue, an unusual location for minor salivary gland neoplasms. Eleven months after excision and nodal dissection, there is no evidence of recurrence or metastasis.
Keywords: Mucoepidermoid carcinoma; Salivary gland; Sialadenoma papilliferum.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sialadenoma papilliferum of a minor salivary gland with transformation to mucoepidermoid carcinoma.J Postgrad Med. 2022 Apr-Jun;68(2):112-114. doi: 10.4103/jpgm.jpgm_912_21. J Postgrad Med. 2022. PMID: 35381752 Free PMC article.
-
Sialadenoma papilliferum.J Oral Surg. 1980 Sep;38(9):691-3. J Oral Surg. 1980. PMID: 6931892
-
Sialadenoma papilliferum in a young patient: a case report and review of the literature.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007 Mar;103(3):e51-4. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.01.012. Epub 2006 Jul 27. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007. PMID: 17321439 Review.
-
Multiple malignant salivary gland neoplasms: mucoepidermoid carcinoma of palate and adenoid cystic carcinoma of floor of mouth.Head Neck Pathol. 2008 Mar;2(1):41-8. doi: 10.1007/s12105-007-0026-1. Epub 2007 Dec 6. Head Neck Pathol. 2008. PMID: 20614341 Free PMC article.
-
Low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the intraoral minor salivary glands with cervical metastasis: report of 2 cases and review of the literature.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010 Jun;68(6):1396-9. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2009.12.019. Epub 2010 Apr 3. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20363544 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Primary mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the breast arising in adenomyoepithelioma.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 Mar 23;15(3):e247281. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-247281. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35321911 Free PMC article.
-
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the posterior-lateral border of tongue: a rare presentation.BMJ Case Rep. 2017 Oct 24;2017:bcr2017221521. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221521. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29066652 Free PMC article.
-
Sialadenoma papilliferum of the tongue mimicking a malignant tumor.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 May-Jun;79(3):404. doi: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130071. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23743761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sialadenoma Papilliferum with Inverted Pattern in a Young Patient: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2015 Sep 28;16:663-6. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.893987. Am J Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26414128 Free PMC article.
-
The First Successful Case of Transoral Robotic Surgery in a Patient with Sialadenoma Papilliferum.Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Sep;28(88):357-361. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 27738613 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

