Peak oxygen consumption and long-term all-cause mortality in nonsmall cell lung cancer
- PMID: 20597134
- PMCID: PMC5399980
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.25396
Peak oxygen consumption and long-term all-cause mortality in nonsmall cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Identifying strong markers of prognosis is critical to optimize treatment and survival outcomes in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The authors investigated the prognostic significance of preoperative cardiorespiratory fitness (peak oxygen consumption [VO(2peak)]) among operable candidates with NSCLC.
Methods: By using a prospective design, 398 patients with potentially resectable NSCLC enrolled in Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9238 were recruited between 1993 and 1998. Participants performed a cardiopulmonary exercise test to assess VO(2peak) and were observed until death or June 2008. Cox proportional models were used to estimate the risk of all-cause mortality according to cardiorespiratory fitness category defined by VO(2peak) tertiles (<0.96 of 0.96-1.29/>1.29 L/min⁻¹) with adjustment for age, sex, and performance status.
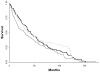
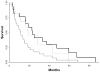
Results: Median follow-up was 30.8 months; 294 deaths were reported during this period. Compared with patients achieving a VO(2peak) <0.96 L/min⁻¹, the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for all-cause mortality was 0.64 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46-0.88) for a VO(2peak) of 0.96 to 1.29 L/min⁻¹, and 0.56 (95% CI, 0.39-0.80) for a VO(2peak) of >1.29 L/min⁻¹) (P(trend) = .0037). The corresponding HRs for resected patients were 0.66 (95% CI, 0.46-0.95) and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.40-0.89) relative to the lowest VO(2peak) category (P(trend) = .0247), respectively. For nonresected patients, the HRs were 0.78 (95% CI, 0.34-1.79) and 0.39 (95% CI, 0.16-0.94) relative to the lowest category (P(trend) = .0278).
Conclusions: VO(2peak) is a strong independent predictor of survival in NSCLC that may complement traditional markers of prognosis to improve risk stratification and prognostication.
© 2010 American Cancer Society.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58(2):71–96. - PubMed
-
- Blanchon F, Grivaux M, Asselain B, Lebas FX, Orlando JP, Piquet J, et al. 4-year mortality in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: development and validation of a prognostic index. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(10):829–36. - PubMed
-
- Brundage MD, Davies D, Mackillop WJ. Prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer: a decade of progress. Chest. 2002;122(3):1037–57. - PubMed
-
- Jones LW, Eves ND, Haykowsky M, Joy AA, Douglas PS. Cardiorespiratory exercise testing in clinical oncology research: systematic review and practice recommendations. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(8):757–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

