Differential effects of central injections of D1 and D2 receptor agonists and antagonists on male sexual behavior in Japanese quail
- PMID: 20597974
- PMCID: PMC2928651
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07257.x
Differential effects of central injections of D1 and D2 receptor agonists and antagonists on male sexual behavior in Japanese quail
Abstract
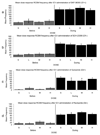
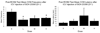
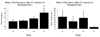
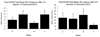
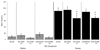
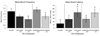
A key brain site in the control of male sexual behavior is the medial pre-optic area (mPOA) where dopamine stimulates both D1 and D2 receptor subtypes. Research completed to date in Japanese quail has only utilized systemic injections and therefore much is unknown about the specific role played by dopamine in the brain and mPOA in particular. The present study investigated the role of D1 and D2 receptors on male sexual behavior by examining how intracerebroventricular injections and microinjections into the mPOA of D1 and D2 agonists and antagonists influenced appetitive and consummatory aspects of sexual behavior in male quail. Experiments 1 and 2 investigated the effects of intracerebroventricular injections at three doses of D1 or D2 agonists and antagonists. The results indicated that D1 receptors facilitated consummatory male sexual behavior, whereas D2 receptors inhibited both appetitive and consummatory behaviors. Experiment 3 examined the effects of the same compounds specifically injected in the mPOA and showed that, in this region, both receptors stimulated male sexual behaviors. Together, these data indicated that the stimulatory action of dopamine in the mPOA may require a combined activation of D1 and D2 receptors. Finally, the regulation of male sexual behavior by centrally infused dopaminergic compounds in a species lacking an intromittent organ suggested that dopamine action on male sexual behavior does not simply reflect the modulation of genital reflexes due to general arousal, but relates to the central control of sexual motivation. Together, these data support the claim that dopamine specifically regulates male sexual behavior.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential effects of D1 and D2 dopamine-receptor agonists and antagonists on appetitive and consummatory aspects of male sexual behavior in Japanese quail.Physiol Behav. 1997 Sep;62(3):571-80. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(97)00163-7. Physiol Behav. 1997. PMID: 9272666
-
Dopamine receptors play distinct roles in sexual behavior expression of rats with a different sexual motivational tone.Behav Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;25(7):684-94. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000086. Behav Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25171081
-
Differential regulation of female sexual behaviour by dopamine agonists in the medial preoptic area.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010 Dec;97(2):284-92. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2010.08.012. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010. PMID: 20807549
-
Role of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens in mediating reward.J Neurosci. 1997 Nov 1;17(21):8580-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-21-08580.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9334429 Free PMC article.
-
Topography in the preoptic region: differential regulation of appetitive and consummatory male sexual behaviors.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2007 Oct;28(4):161-78. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2007.05.003. Epub 2007 Jun 8. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17624413 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pleasure seeking and birdsong.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011 Oct;35(9):1837-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.12.017. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011. PMID: 21251924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine release in the medial preoptic area is related to hormonal action and sexual motivation.Behav Neurosci. 2010 Dec;124(6):773-9. doi: 10.1037/a0021490. Behav Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21133533 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroestrogens rapidly regulate sexual motivation but not performance.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 2;33(1):164-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2557-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23283331 Free PMC article.
-
Review: neuroestrogen regulation of socio-sexual behavior of males.Front Neurosci. 2014 Oct 13;8:323. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00323. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25352775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential relationships between D1 and D2 dopamine receptor expression in the medial preoptic nucleus and sexually-motivated song in male European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris).Neuroscience. 2015 Aug 20;301:289-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.011. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26079111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Absil P, Das S, Balthazart J. Effects of apomorphine on sexual behavior in male quail. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1994;47:77–88. - PubMed
-
- Adkins-Regan E. Neuroanatomy of sexual behavior in the male Japanese quail from top to bottom. Poultry and Avian Biology Reviews. 1996;7:193–204.
-
- Adkins EK, Adler NT. Hormonal control of behavior in the Japanese quail. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1972;81:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Ball GF, Balthazart J. Neuroendocrine Mechanisms Regulating Reproductive Cycles and Reproductive Behavior in Birds. In: Pfaff DW, Arnold AP, Etgen AM, Fahrback SE, Rubin RT, editors. Hormones, Brain, Behavior. San Diego, California: Academic Press; 2002. pp. 649–798.
-
- Ball GF, Balthazart J. Hormonal regulation of brain circuits mediating male sexual behavior in birds. Physiol Behav. 2004;83:329–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

