Fine mapping of QTL for prepulse inhibition in LG/J and SM/J mice using F(2) and advanced intercross lines
- PMID: 20597988
- PMCID: PMC3749925
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00613.x
Fine mapping of QTL for prepulse inhibition in LG/J and SM/J mice using F(2) and advanced intercross lines
Abstract
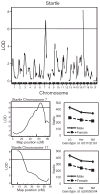
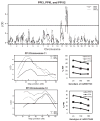
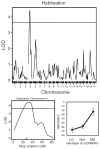
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the startle response is a measure of sensorimotor gating, a process that filters out extraneous sensory, motor and cognitive information. Humans with neurological and psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder and Huntington's disease, exhibit a reduction in PPI. Habituation of the startle response is also disrupted in schizophrenic patients. In order to elucidate the genes involved in sensorimotor gating, we phenotyped 472 mice from an F(2) cross between LG/J × SM/J for PPI and genotyped these mice genome-wide using 162 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. We used prepulse intensity levels that were 3, 6 and 12 dB above background (PPI3, PPI6 and PPI12, respectively). We identified a significant quantitative trait locus (QTL) on chromosome 12 for all three prepulse intensities as well as a significant QTL for both PPI6 and PPI12 on chromosome 11. We identified QTLs on chromosomes 7 and 17 for the startle response when sex was included as an interactive covariate and found a QTL for habituation of the startle response on chromosome 4. We also phenotyped 135 mice from an F(34) advanced intercross line (AIL) between LG/J × SM/J for PPI and genotyped them at more than 3000 SNP markers. Inclusions of data from the AIL mice reduced the size of several of these QTLs to less than 5 cM. These results will be useful for identifying genes that influence sensorimotor gaiting and show the power of AIL for fine mapping of QTLs.
© 2010 The Authors. Genes, Brain and Behavior © 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Figures
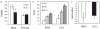
Similar articles
-
Genomic survey of prepulse inhibition in mouse chromosome substitution strains.Genes Brain Behav. 2009 Nov;8(8):806-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2009.00526.x. Epub 2009 Jul 21. Genes Brain Behav. 2009. PMID: 19694817 Free PMC article.
-
Provisional mapping of quantitative trait loci modulating the acoustic startle response and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002 Nov;27(5):765-81. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00333-0. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12431851
-
Short-term selective breeding for high and low prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response; pharmacological characterization and QTL mapping in the selected lines.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008 Oct;90(4):525-33. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.04.004. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008. PMID: 18513787 Free PMC article.
-
Human studies of prepulse inhibition of startle: normal subjects, patient groups, and pharmacological studies.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001 Jul;156(2-3):234-58. doi: 10.1007/s002130100810. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11549226 Review.
-
Using an animal model of deficient sensorimotor gating to study the pathophysiology and new treatments of schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 1998;24(2):285-301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a033326. Schizophr Bull. 1998. PMID: 9613626 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association for methamphetamine sensitivity in an advanced intercross mouse line.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Feb;11(1):52-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2011.00747.x. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22032291 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray-assisted fine mapping of quantitative trait loci on chromosome 15 for susceptibility to seizure-induced cell death in mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Dec;38(12):3679-90. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12351. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24001120 Free PMC article.
-
Using Heterogeneous Stocks for Fine-Mapping Genetically Complex Traits.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2018:233-247. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9581-3_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31228160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous Stock Populations for Analysis of Complex Traits.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1488:31-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6427-7_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27933519 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic models of sensorimotor gating: relevance to neuropsychiatric disorders.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2012;12:251-318. doi: 10.1007/7854_2011_195. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22367921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anokhin AP, Heath AC, Myers E, Ralano A, Wood S. Genetic influences on prepulse inhibition of startle reflex in humans. Neurosci Lett. 2003;1:45–48. - PubMed
-
- Braff DL, Grillon C, Geyer MA. Gating and habituation of the startle reflex in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992;3:206–215. - PubMed
-
- Broman KW, Sen S. A Guide to QTL Mapping with R/qtl. Springer; New York: 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

