Stretch and inflammation-induced Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF/Visfatin) and Interleukin-8 in amniotic epithelial cells
- PMID: 20598369
- PMCID: PMC2921847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2010.06.007
Stretch and inflammation-induced Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF/Visfatin) and Interleukin-8 in amniotic epithelial cells
Abstract
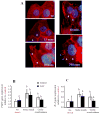
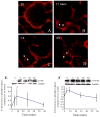
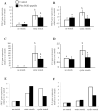
Preterm birth continues to be a growing problem in the USA. Although approximately half of preterm births are caused by intrauterine infection, uterine over-distension is also a cause. In this study we have compared the effects of static stretch, cyclic stretch/release and an inflammatory stimulus alone and in combination on the expression of Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF) and IL-8 in primary amniotic epithelial cells (AEC). We then sought to identify some of the mechanism(s) by which these cells respond to stretching stimuli. We show that cyclic stretch/release is a more robust stimulus for both PBEF and IL-8 than static stretch. Cyclic stretch/release increased both intracellular and secreted PBEF and a combination of both types of stretch was a more robust stimulus to PBEF that IL-8. However, when an inflammatory stimulus (IL-1beta) was added to either kind of stretch, the effect on IL-8 was much greater than that on PBEF. Thus, different kinds of stretch affect the expression of these two cytokines from AEC, but inflammation is a much stronger stimulus of IL-8 than PBEF, agreeing with its primary role as a chemokine. Although the AEC showed morphological signs of increased cellular stress during stretching, blocking reactive oxygen species (ROS) had little effect. However, blocking integrin binding to fibronectin significantly reduced the responses of both PBEF and IL-8 to cyclic stretch/release. The increased PBEF, both intracellularly and secreted, suggests that it functions both to increase the metabolism of the cells, at the same time as stimulating further the cytokine cascade leading to parturition.
Figures
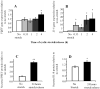
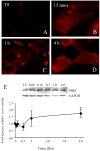
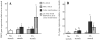
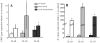
Similar articles
-
Chronic stretching of amniotic epithelial cells increases pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF/visfatin) expression and protects them from apoptosis.Placenta. 2008 Mar;29(3):255-65. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2007.12.008. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Placenta. 2008. PMID: 18272217
-
Pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF/Visfatin) gene expression is modulated by NF-kappaB and AP-1 in human amniotic epithelial cells.Placenta. 2007 Apr;28(4):305-14. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2006.03.011. Epub 2006 May 15. Placenta. 2007. PMID: 16701870
-
Pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor, a novel cytokine of human fetal membranes.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Oct;187(4):1051-8. doi: 10.1067/mob.2002.126295. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002. PMID: 12389004
-
Stretching, mechanotransduction, and proinflammatory cytokines in the fetal membranes.Reprod Sci. 2007 Dec;14(8 Suppl):35-41. doi: 10.1177/1933719107310763. Reprod Sci. 2007. PMID: 18089608 Review.
-
Pre-B cell colony enhancing factor (PBEF), a cytokine with multiple physiological functions.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Oct;24(5):433-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23787158 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-B-cell colony enhancing factor regulates the alveolar epithelial sodium-water transport system through the ERK and AKT pathways.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Sep 15;11(9):5824-5835. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31632551 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the innate immune response by fibronectin: synergism between the III-1 and EDA domains.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 22;9(7):e102974. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102974. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25051083 Free PMC article.
-
The entry of fetal and amniotic fluid components into the uterine vessel circulation leads to sterile inflammatory processes during parturition.Front Immunol. 2012 Oct 23;3:321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00321. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23109934 Free PMC article.
-
Stretch Causes Cell Stress and the Downregulation of Nrf2 in Primary Amnion Cells.Biomolecules. 2022 May 31;12(6):766. doi: 10.3390/biom12060766. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740891 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble ST2, a modulator of the inflammatory response, in preterm and term labor.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014 Jan;27(2):111-21. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2013.806894. Epub 2013 Nov 13. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014. PMID: 23688338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- March of Dimes. 2000. http://marchofdimes.com/peristats/
-
- Christiaens I, Zaragoza DB, Guilbert L, Robertson SA, Mitchell BF, Olson DM. Inflammatory processes in preterm and term parturition. J of Reprod Immunol. 2008;79:50–7. - PubMed
-
- Keelan JA, Blumenstein M, Helliwell RJA, Sato TA, Marvin KW, Mitchell MD. Cytokines, prostaglandins and parturition--a review. Placenta. 2003;24(Suppl A):S33–46. - PubMed
-
- Keelan JA, Marvin KW, Sato TA, Coleman M, McCowan LM, Mitchell MD. Cytokine abundance in placental tissues: evidence of inflammatory activation in gestational membranes with term and preterm parturition. Am J Obstet and Gynecol. 1999;181:1530–6. - PubMed
-
- Millar LK, Stollberg J, DeBuque L, Bryant-Greenwood G. Fetal membrane distention: determination of the intrauterine surface area and distention of the fetal membranes preterm and at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182:128–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

