The who and where of HIV in rural Malawi: Exploring the effects of person and place on individual HIV status
- PMID: 20598623
- PMCID: PMC3454472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2010.06.004
The who and where of HIV in rural Malawi: Exploring the effects of person and place on individual HIV status
Abstract
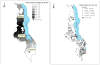
Few spatial studies explore relationships between people and place in sub-Saharan Africa or in the context of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This paper uses individual-level demographic and behavioral data linked to area-level, spatially referenced socio-economic and access data to examine how the relationships between area- and individual-level risks and individual HIV status vary in rural Malawi. The political economy of health framework guides interpretation. Geographically weighted regression models show significant, local-level variation indicating that area-level factors drive patterns of HIV above individual-level contributions. In distinct locations, women who live further from health clinics, major roads, and major cities are less likely to be infected. For men, HIV status is strongly associated with migration patterns in specific areas. Local-level, gender-specific approaches to HIV prevention are necessary in high risk areas.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Adimora AA, Schoenbach VJ. Contextual factors and the black-white disparity in heterosexual HIV transmission. Epidemiology. 2002;13:707–712. - PubMed
-
- Armour L. Trying to survive in times of poverty and AIDS: women and multiple-partner sex in Malawi. Aids Care-Psychological and Socio-Medical Aspects of AIDS/HIV. 2006;18:404–404.
-
- Barden-O’Fallon JL, deGraft-Johnson J, Bisika T, Sulzbach S, Benson A, Tsui AO. Factors associated with hiv/aids knowledge and risk perception in rural Malawi. Aids and Behavior. 2004;8:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Benefo KD. Determinants of Zambian Men’s Extra-Marital Sex: A Multi-level Analysis. Archives of Sexual Behavior. 2008;37:517–529. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical