Virtual fragment screening for novel inhibitors of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
- PMID: 20598892
- PMCID: PMC2939770
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.05.077
Virtual fragment screening for novel inhibitors of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
Abstract
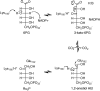
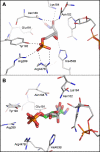
The enzyme 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is a potential drug target for the parasitic protozoan Trypanosoma brucei, the causative organism of human African trypanosomiasis. This enzyme has a polar active site to accommodate the phosphate, hydroxyl and carboxylate groups of the substrate, 6-phosphogluconate. A virtual fragment screen was undertaken of the enzyme to discover starting points for the development of inhibitors which are likely to have appropriate physicochemical properties for an orally bioavailable compound. A virtual screening library was developed, consisting of compounds with functional groups that could mimic the phosphate group of the substrate, but which have a higher pKa. Following docking, hits were clustered and appropriate compounds purchased and assayed against the enzyme. Three fragments were identified that had IC50 values in the low micromolar range and good ligand efficiencies. Based on these initial hits, analogues were procured and further active compounds were identified. Some of the fragments identified represent potential starting points for a medicinal chemistry programme to develop potent drug-like inhibitors of the enzyme.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

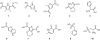

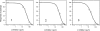
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of substrate-based inhibitors of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase as potential drugs against African trypanosomiasis.Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 Jul 17;11(14):3205-14. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(03)00191-3. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12818683
-
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase: a target for drugs in African trypanosomes.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Oct;11(19):2639-50. doi: 10.2174/0929867043364441. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15544466 Review.
-
6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from Trypanosoma brucei. Kinetic analysis and inhibition by trypanocidal drugs.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Sep 15;240(3):592-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0592h.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8856059
-
Selective inhibition of Trypanosoma brucei 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase by high-energy intermediate and transition-state analogues.J Med Chem. 2004 Jun 17;47(13):3427-37. doi: 10.1021/jm031066i. J Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15189039
-
Cruzain inhibitors: efforts made, current leads and a structural outlook of new hits.Drug Discov Today. 2015 Jul;20(7):890-8. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Drug Discov Today. 2015. PMID: 25697479 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational approaches for drug discovery against trypanosomatid-caused diseases.Parasitology. 2020 May;147(6):611-633. doi: 10.1017/S0031182020000207. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Parasitology. 2020. PMID: 32046803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Antigens for Development of a Serological Test for Human African Trypanosomiasis.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0168074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168074. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27936225 Free PMC article.
-
6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase and its crystal structures.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2022 Mar 1;78(Pt 3):96-112. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X22001091. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35234135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IspE inhibitors identified by a combination of in silico and in vitro high-throughput screening.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035792. Epub 2012 Apr 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563402 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Leishmania donovani 6-Phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase and Inhibition by Phosphine Gold(I) Complexes: A Potential Approach to Leishmaniasis Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 11;24(10):8615. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108615. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Available from: <http://www.who.int/trypanosomiasis_african/disease/en/index.html>.
-
- Barrett M.P. Parasitol. Today. 1997;13:11. - PubMed
-
- Dardonville C., Rinaldi E., Barrett M.P., Brun R., Gilbert I.H., Hanau S. J. Med. Chem. 2004;47:3427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

