Treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitor attenuates MAP kinase mediated liver injury in a lethal model of septic shock
- PMID: 20599223
- PMCID: PMC4894321
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.04.024
Treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitor attenuates MAP kinase mediated liver injury in a lethal model of septic shock
Abstract
Background: Despite global efforts to improve the treatment of sepsis, it remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in intensive care units. We have previously shown that suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, markedly improves survival in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced shock. SAHA has anti-inflammatory properties that have not been fully characterized. The liver plays an important role in the production of acute phase reactants involved in the inflammatory cascade and is also one of the major organs that can become dysfunctional in septic shock. The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of SAHA treatment on MAP kinases and associated inflammatory markers in murine liver after LPS-induced injury.
Methods: C57B1/6J mice were randomly divided into three groups: (A) experimental-given intraperitoneal (i.p.) SAHA (50 mg/kg) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) vehicle solution (n = 12); (B) control- given vehicle only (n = 12), and; (C) sham-given no treatment (n = 7). Two hours later, experimental and control mice were injected with LPS (20 mg/kg, i.p.) and experimental mice received a second dose of SAHA. Livers were harvested at 3, 24, and 48 h for analysis of inflammatory markers using Western Blot, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) techniques.
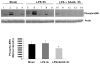
Results: After 3 h, the livers of animals treated with SAHA showed significantly (P < 0.05) decreased expression of the pro-inflammatory MAP kinases phosphorylated p38, phosphorylated ERK, myeloperoxidase and interleukin-6, and increased levels of the anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 compared with controls. Phospho-p38 expression remained low in the SAHA treated groups at 24 and 48 h.
Conclusion: Administration of SAHA is associated with attenuation of MAPK activation and alteration of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers in murine liver after a lethal LPS insult. The suppression of MAPK activity is rapid (within 3 h), and is sustained for up to 48 h post-treatment. These results may in part account for the improvement in survival shown in this model.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Novel pharmacologic treatment attenuates septic shock and improves long-term survival.Surgery. 2013 Aug;154(2):206-13. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.04.003. Surgery. 2013. PMID: 23889949 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid against LPS-induced septic shock in rodents.Shock. 2009 Nov;32(5):517-23. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181a44c79. Shock. 2009. PMID: 19295477
-
Surviving lethal septic shock without fluid resuscitation in a rodent model.Surgery. 2010 Aug;148(2):246-54. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Surgery. 2010. PMID: 20561658 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid against lipopolysaccharide-induced liver damage in rodents.J Surg Res. 2015 Apr;194(2):544-550. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.10.056. Epub 2014 Nov 6. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25479907 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of citrullinated histone H3 as a potential serum protein biomarker in a lethal model of lipopolysaccharide-induced shock.Surgery. 2011 Sep;150(3):442-51. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.07.003. Surgery. 2011. PMID: 21878229 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps, damage-associated molecular patterns, and cell death during sepsis.Acute Med Surg. 2013 Nov 15;1(1):2-9. doi: 10.1002/ams2.10. eCollection 2014 Jan. Acute Med Surg. 2013. PMID: 29930815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valproic acid alleviates memory deficits and attenuates amyloid-β deposition in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Feb;51(1):300-12. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8751-4. Epub 2014 May 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24854198
-
Epigenetics in Sepsis: Understanding Its Role in Endothelial Dysfunction, Immunosuppression, and Potential Therapeutics.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 18;10:1363. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01363. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31275313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel pharmacologic treatment attenuates septic shock and improves long-term survival.Surgery. 2013 Aug;154(2):206-13. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.04.003. Surgery. 2013. PMID: 23889949 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: A Novel Strategy for Neuroprotection and Cardioprotection Following Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jun 2;9(11):e016349. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016349. Epub 2020 May 22. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32441201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rivers EP, Coba V, Whitmill M. Early goal-directed therapy in severe sepsis and septic shock: A contemporary review of the literature. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008;21:128. - PubMed
-
- Takemura R, Werb Z. Secretory products of macrophages and their physiological functions. Am J Physiol. 1984;246(1 Pt 1):C1. - PubMed
-
- Kishore R, McMullen MR, Nagy LE. Stabilization of tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA by chronic ethanol: Role of A + U-rich elements and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41930. - PubMed
-
- Lee MR, Dominguez C. MAP kinase p38 inhibitors: Clinical results and an intimate look at their interactions with p38alpha protein. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12:2979. - PubMed
-
- Lee JC, Laydon JT, McDonnell PC, et al. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature. 1994;372:739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

