Structural and dynamic determinants of ligand binding and regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 by pathological activator p25 and inhibitory peptide CIP
- PMID: 20599546
- PMCID: PMC2919306
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.06.040
Structural and dynamic determinants of ligand binding and regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 by pathological activator p25 and inhibitory peptide CIP
Abstract
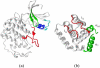
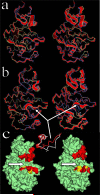
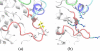
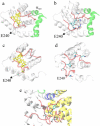
The crystal structure of the cdk5/p25 complex has provided information on possible molecular mechanisms of the ligand binding, specificity, and regulation of the kinase. Comparative molecular dynamics simulations are reported here for physiological conditions. This study provides new insight on the mechanisms that modulate such processes, which may be exploited to control pathological activation by p25. The structural changes observed in the kinase are stabilized by a network of interactions involving highly conserved residues within the cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) family. Collective motions of the proteins (cdk5, p25, and CIP) and their complexes are identified by principal component analysis, revealing two conformational states of the activation loop upon p25 complexation, which are absent in the uncomplexed kinase and not apparent from the crystal. Simulations of the uncomplexed inhibitor CIP show structural rearrangements and increased flexibility of the interfacial loop containing the critical residue E240, which becomes fully hydrated and available for interactions with one of several positively charged residues in the kinase. These changes provide a rationale for the observed high affinity and enhanced inhibitory action of CIP when compared to either p25 or the physiological activators of cdk5.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

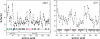
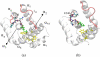
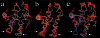
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the interaction of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 with activator p25 and with p25-derived inhibitor CIP.J Comput Biol. 2010 May;17(5):707-21. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2009.0202. J Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20500023
-
Explaining the inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 by peptides derived from p25 with molecular dynamics simulations and MM-PBSA.J Mol Model. 2010 Jan;16(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s00894-009-0514-1. Epub 2009 May 23. J Mol Model. 2010. PMID: 19466465
-
Different mechanisms of CDK5 and CDK2 activation as revealed by CDK5/p25 and CDK2/cyclin A dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 17;281(11):7271-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509699200. Epub 2006 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407256
-
Peptides derived from Cdk5 activator p35, specifically inhibit deregulated activity of Cdk5.Biotechnol J. 2007 Aug;2(8):978-87. doi: 10.1002/biot.200700057. Biotechnol J. 2007. PMID: 17526058 Review.
-
Neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5: role in nervous system function and its specific inhibition by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.020. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023357 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection and characterization of nonspecific, sparsely populated binding modes in the early stages of complexation.J Comput Chem. 2015 May 15;36(13):983-95. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23883. Epub 2015 Mar 18. J Comput Chem. 2015. PMID: 25782918 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamic simulations give insight into the mechanism of binding between 2-aminothiazole inhibitors and CDK5.J Mol Model. 2013 Jun;19(6):2635-45. doi: 10.1007/s00894-013-1815-y. Epub 2013 Mar 23. J Mol Model. 2013. PMID: 23525963
-
Consensus models for CDK5 inhibitors in silico and their application to inhibitor discovery.Mol Divers. 2015 Feb;19(1):149-62. doi: 10.1007/s11030-014-9561-3. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Mol Divers. 2015. PMID: 25511641
-
Multi-Target β-Protease Inhibitors from Andrographis paniculata: In Silico and In Vitro Studies.Plants (Basel). 2019 Jul 17;8(7):231. doi: 10.3390/plants8070231. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31319560 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of displacement of a catalytically essential loop from the active site of mammalian fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.Biochemistry. 2013 Aug 6;52(31):5206-16. doi: 10.1021/bi400532n. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23844654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Living with or without cyclins and cyclin-dependent Kinases. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2699. - PubMed
-
- Lee HY, Jung H, Jang JH, Suh PG, Ryu SH. Cdk5 phosphorylates PLD2 to mediate EGF-dependent insulin secretion. Cell Signal. 2008;20:1787. - PubMed
-
- Hisanaga S, Saito T. The regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity through the metabolism of p35 or p39 Cdk5 activator. Neurosignals. 2003;12:221. - PubMed
-
- Kwon YT, Tsai L-H. A novel disruption of cortical development in p35 (-/-) Mice Distinct from Reeler. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998;395:510. - PubMed
-
- Lee MS, Kwon YT, Li M, Peng J, Friedlander RM, Tsai LH. Neurotoxicity induces cleavage of p35 to p25 by Calpain. Nature. 2000;405:360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

