Systemic lupus erythematosus and increased risk to develop B cell malignancies: role of the p200-family proteins
- PMID: 20599558
- PMCID: PMC2926135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2010.06.008
Systemic lupus erythematosus and increased risk to develop B cell malignancies: role of the p200-family proteins
Abstract
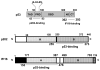
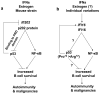
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease, develops at a female-to-male ratio of 10:1. Increased serum levels of type I interferons (IFN-alpha/beta) and induction of "IFN-signature" genes are associated with an active SLE disease in patients. Moreover, SLE patients exhibit three- to four-fold increase in the risk of developing malignancies involving B cells, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL). Interestingly, homozygous mice expressing a deletion mutant (the proline-rich domain deleted) of the p53 develop various types of spontaneous tumors, particularly of B cell origin upon aging. The deletion is associated with defects in transcriptional activation of genes by p53 and inhibition of DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Notably, increased levels of the p202 protein, which is encoded by the p53-repressible interferon-inducible Ifi202 gene, in B cells of female mice are associated with defects in B cell apoptosis, inhibition of the p53-mediated transcription of pro-apoptotic genes, and increased lupus susceptibility. In this review we discuss how increased levels of the p202 protein (and its human functional homologue IFI16 protein) in B cells increase lupus susceptibility and are likely to increase the risk of developing certain B cell malignancies. A complete understanding of the molecular mechanisms that regulate B cell homeostasis is necessary to identify SLE patients with an increased risk to develop B cell malignancies.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996;85:303–6. - PubMed
-
- Pisetsky DS. The role of innate immunity in the induction of autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2008;8:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Baccala R, Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN. Interferons as pathogenic effectors in autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. 2005;204:9–26. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH. Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:307–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

