The design and validation of a novel phenotypic assay to determine HIV-1 coreceptor usage of clinical isolates
- PMID: 20599562
- PMCID: PMC2930119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.06.012
The design and validation of a novel phenotypic assay to determine HIV-1 coreceptor usage of clinical isolates
Abstract
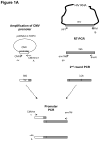
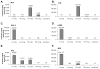
A phenotypic assay to determine coreceptor usage of HIV-1 has been developed for rapid testing of clinical samples. The assay is based on the synthesis of viral stock from full-length env amplicons isolated from patient's plasma. Pseudoviral stock is generated rapidly by using an overlapping PCR method to assemble a CMV promoter to env, followed by co-transfection into producer cells with a HIV plasmid (pNL4-3.Luc.R(-)E(-)) containing a non-functional env. The coreceptor used by the viral quasispecies is tested by infection into U87.CD4.CCR5 and U87.CD4.CXCR4 cells. Viral entry is indicated by the expression of the luciferase gene in relative light units (RLU). The use of CXCR4 coreceptor by minor variants is confirmed with sufficient suppression of RLU by a CXCR4 inhibitor. Two statistical tests are employed to confirm viral entry. This assay accurately assigned coreceptor usage of isolates of various subtypes and in the majority of samples of various viral loads. The sensitivity to detect minor species of CXCR4-using env is 1% at higher viral loads and 5% at less than 1,000 copies/ml. This assay provides a sensitive, efficient and relatively low-cost approach suitable for use by research laboratories for assessing HIV-1 coreceptor usage of plasma samples.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

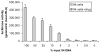
References
-
- Braun P, Wiesmann F. Phenotypic assays for the determination of coreceptor tropism in HIV-1 infected individuals. Eur J Med Res. 2007;12:463–72. - PubMed
-
- Coakley E, Reeves JD, Huang W, Mangas-Ruiz M, Maurer I, Harskamp AM, Gupta S, Lie Y, Petropoulos CJ, Schuitemaker H, van 't Wout AB. Comparison of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tropism profiles in clinical samples by the Trofile and MT-2 assays. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:4686–93. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cocchi F, DeVico AL, Garzino-Demo A, Cara A, Gallo RC, Lusso P. The V3 domain of the HIV-1 gp120 envelope glycoprotein is critical for chemokine-mediated blockade of infection. Nat Med. 1996;2:1244–7. - PubMed
-
- Fang G, Zhu G, Burger H, Keithly JS, Weiser B. Minimizing DNA recombination during long RT-PCR. J Virol Methods. 1998;76:139–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

