Functional differences in the cytochrome P450 1 family enzymes from zebrafish (Danio rerio) using heterologously expressed proteins
- PMID: 20599672
- PMCID: PMC2945726
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.06.018
Functional differences in the cytochrome P450 1 family enzymes from zebrafish (Danio rerio) using heterologously expressed proteins
Abstract
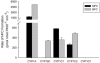
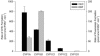
Mammalian cytochrome P450 1 (CYP1) genes are well characterized, but in other vertebrates only the functions of CYP1A genes have been well studied. We determined the catalytic activity of zebrafish CYP1A, CYP1B1, CYP1C1, CYP1C2, and CYP1D1 proteins using 11 fluorometric substrates and benzo[a]pyrene (BaP). The resorufin-based substrates, 7-ethoxyresorufin, 7-methoxyresorufin, and 7-benzyloxyresorufin, were well metabolized by all CYP1s except CYP1D1. CYP1A metabolized nearly all substrates tested, although rates for non-resorufin substrates were typically lower than resorufin-based substrates. Zebrafish CYP1s did not metabolize 7-benzyloxyquinoline, 3-[2-(N,N-diethyl-N-methylamino)ethyl]-7-methoxy-4-methylcoumarin or 7-methoxy-4-(aminomethyl)-coumarin. CYP1B1 and CYP1C2 had the highest rates of BaP metabolism. 3-Hydroxy-BaP was a prominent metabolite for all but CYP1D1. CYP1A showed broad specificity and had the highest metabolic rates for nearly all substrates. CYP1C1 and CYP1C2 had similar substrate specificity. CYP1D1 had very low activities for all substrates except BaP, and a different regioselectivity for BaP, suggesting that CYP1D1 function may be different from other CYP1s.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
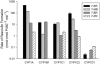
References
-
- Guengerich FP. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001;14:611–650. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Gaikwad NW, Olson K, Zahid M, Cavalieri EL, Rogan EG. Metabolism. 2007;56:887–894. - PubMed
-
- McGinnity DF, Griffin SJ, Moody GC, Voice M, Hanlon S, Friedberg T, Riley RJ. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1999;27:1017–1023. - PubMed
-
- Blom MJ, Wassink MG, Kloosterboer HJ, Ederveen AG, Lambert JG, Goos HJ. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001;29:76–81. - PubMed
-
- Nebert DW, Dalton TP, Okey AB, Gonzalez FJ. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:23847–23850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

