Differential effects of Heparitinase I and Heparitinase III on endothelial tube formation in vitro
- PMID: 20599743
- PMCID: PMC2924581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.055
Differential effects of Heparitinase I and Heparitinase III on endothelial tube formation in vitro
Abstract
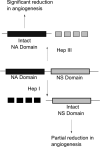
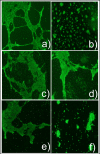
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) play vital roles in many steps of angiogenesis under physiological and pathological conditions. HSPGs on endothelial cell surfaces act as co-receptors for a variety of pro-angiogenic growth factors such as FGF and VEGF and anti-angiogenic factors such as endostatin. However, the fine structural requirements of these binding interactions are dependent on the sulfation patterns of HSPGs. Previous studies have shown that Heparitinases, heparin lyases isolated from Flavobacterium heparinum, can cleave heparan sulfate chains. These enzymes have been shown to reduce tumor-derived neovascularization in vivo in mice. However, the results from these experiments could not conclusively pinpoint the origin of the HS fragments. Thus, in this study we utilized an in vitro assay to assess the differential effects of Heparitinase I (Hep I) and Heparitinase III (Hep III) on endothelial tube formation. Hep III was found to be a more potent inhibitor of tube formation than Hep I. In conclusion, differential cleavage of endothelial cell surface bound HS can affect the extent of inhibition of tube formation.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic inhibitors affect tumor-associated angiogenesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jan 7;404(1):86-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.11.069. Epub 2010 Nov 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21094131 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and substrate specificity of heparitinase I and heparitinase II from Flavobacterium heparinum. Analyses of the heparin and heparan sulfate degradation products by 13C NMR spectroscopy.J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16807-13. J Biol Chem. 1990. PMID: 2211596
-
Structural studies on the oligosaccharides isolated from bovine kidney heparan sulphate and characterization of bacterial heparitinases used as substrates.Glycobiology. 1994 Aug;4(4):535-44. doi: 10.1093/glycob/4.4.535. Glycobiology. 1994. PMID: 7827415
-
New insights on the specificity of heparin and heparan sulfate lyases from Flavobacterium heparinum revealed by the use of synthetic derivatives of K5 polysaccharide from E. coli and 2-O-desulfated heparin.Glycoconj J. 1999 Jun;16(6):265-70. doi: 10.1023/a:1007057826179. Glycoconj J. 1999. PMID: 10579695
-
Interaction of angiogenic basic fibroblast growth factor with endothelial cell heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Biological implications in neovascularization.Int J Clin Lab Res. 1996;26(1):15-23. doi: 10.1007/BF02644769. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1996. PMID: 8739851 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and characterization of HepP: a virulence-related Pseudomonas aeruginosa heparinase.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Dec 16;17(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-1141-0. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29246112 Free PMC article.
-
Novel glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic inhibitors affect tumor-associated angiogenesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jan 7;404(1):86-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.11.069. Epub 2010 Nov 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21094131 Free PMC article.
-
Fractone-heparan sulphates mediate FGF-2 stimulation of cell proliferation in the adult subventricular zone.Cell Prolif. 2013 Apr;46(2):137-45. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12023. Cell Prolif. 2013. PMID: 23510468 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel sulfonated small molecules that inhibit vascular tube formation.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jul 1;22(13):4467-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.04.014. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22627041 Free PMC article.
-
A glycan-based approach to therapeutic angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 1;12(8):e0182301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182301. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28763512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogensis: role in regulation of tumor growth. Symp Soc Dev Biol. 1974;30:43–52. - PubMed
-
- Vlodavsky I, Eldor A, Bar-Ner M, Fridman R, Cohen IR, Klagsbrun M. Heparan sulfate degradation in tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;233:201–10. - PubMed
-
- Gallagher JT, Hampson IN. Proteoglycans in cellular differentiation and neoplasia. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984;12:541–3. - PubMed
-
- Guimond S, Maccarana M, Olwin BB, Lindahl U, Rapraeger AC. Activating and inhibitory heparin sequences for FGF-2 (basic FGF). Distinct requirements for FGF-1, FGF-2, and FGF-4. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:23906–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

