Human B-type natriuretic peptide is not degraded by meprin A
- PMID: 20599787
- PMCID: PMC4495880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.015
Human B-type natriuretic peptide is not degraded by meprin A
Abstract
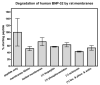
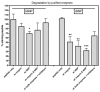
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) combats cardiac stress by reducing blood pressure and ventricular fibrosis. Human BNP is inactivated by unknown cell surface proteases. N-terminal cleavage of mouse BNP by the renal protease meprin A was reported to increase inactivating degradation by a second protease named neprilysin. Since the sequence surrounding the meprin A cleavage site in BNP differs between species, we tested whether meprin A degrades human BNP. Using a recently developed proteolytic bioassay, the ability of various protease inhibitors to block the inactivation of BNP was measured. In rat kidney membranes, inhibitors of meprin A or neprilysin partially or completely blocked inactivation of rat BNP(1-32) when added individually or in combination, respectively. In contrast, neither inhibitor alone or in combination prevented the inactivation of human BNP(1-32) by human kidney membranes. Leupeptin, a serine protease inhibitor, totally blocked inactivation of human BNP by human membranes, substantially blocked the inactivation of rat BNP(1-32) by human membranes, but had no effect on the inactivation of rat BNP(1-32) by rat kidney membranes. Purified neprilysin reduced the bioactivity of rat BNP(1-32) and human BNP. Digestion with both meprin and neprilysis caused the greatest reduction in rat BNP(1-32) but had no effect on the bioactivity of human BNP(1-32). We conclude that meprin A does not degrade BNP in humans and should not be considered a pharmacologic target of the natriuretic peptide system.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Potter LR, Abbey-Hosch S, Dickey DM. Natriuretic peptides, their receptors, and cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent signaling functions. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:47–72. - PubMed
-
- Potter LR. Guanylyl Cyclases. In: Bradshaw RA, Dennis EA, editors. Handbook of Cell Signaling. Oxford: Academic Press; 2009.
-
- Misono KS, Grammer RT, Fukumi H, Inagami T. Rat atrial natriuretic factor: isolation, structure and biological activities of four major peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;123:444–51. - PubMed
-
- Nussenzveig DR, Lewicki JA, Maack T. Cellular mechanisms of the clearance function of type C receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:20952–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

