Pharmacokinetics of OpdA, an organophosphorus hydrolase, in the African green monkey
- PMID: 20599794
- PMCID: PMC2923271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.008
Pharmacokinetics of OpdA, an organophosphorus hydrolase, in the African green monkey
Abstract
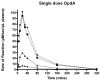
Organophosphorus (OP) pesticides are a broad class of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors that are responsible for tremendous morbidity and mortality worldwide, contributing to an estimated 300,000 deaths annually. Current pharmacotherapy for acute OP poisoning includes the use of atropine, an oxime, and benzodiazepines. However, even with such therapy, the mortality from these agents are as high as 40%. Enzymatic hydrolysis of OPs is an attractive new potential therapy for acute OP poisoning. A number of bacterial OP hydrolases have been isolated. A promising OP hydrolase is an enzyme isolated from Agrobacterium radiobacter, named OpdA. OpdA has been shown to decrease lethality in rodent models of parathion and dichlorvos poisoning. However, pharmacokinetic data have not been obtained. In this study, we examined the pharmacokinetics of OpdA in an African Green Monkey model. At a dose of 1.2mg/kg the half-life of OpdA was approximately 40 min, with a mean residence time of 57 min. As expected, the half-life did not change with the dose of OpdA given: at doses of 0.15 and 0.45 mg/kg, the half-life of OpdA was 43.1 and 38.9 min, respectively. In animals subjected to 5 daily doses of OpdA, the residual activity that was measured 24h after each OpdA dose increased 5-fold for the 0.45 mg/kg dose and 11-fold for the 1.2mg/kg dose. OpdA exhibits pharmacokinetics favorable for the further development as a therapy for acute OP poisoning, particularly for hydrophilic OP pesticides. Future work to increase the half-life of OpdA may be beneficial.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of OpdA, an organophosphorus (OP) hydrolase, prevents lethality in an African green monkey model of acute OP poisoning.Toxicology. 2014 Mar 20;317:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 18. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 24447378 Free PMC article.
-
OpdA, a bacterial organophosphorus hydrolase, prevents lethality in rats after poisoning with highly toxic organophosphorus pesticides.Toxicology. 2008 May 21;247(2-3):88-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.02.005. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18378376 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and efficacy of an organophosphorus hydrolase in a rodent model of methyl-parathion poisoning.Acad Emerg Med. 2010 Jul;17(7):736-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2010.00798.x. Acad Emerg Med. 2010. PMID: 20653588 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oximes in the management of organophosphorus pesticide poisoning.Toxicol Rev. 2003;22(3):165-90. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200322030-00004. Toxicol Rev. 2003. PMID: 15181665 Review.
-
The value of novel oximes for treatment of poisoning by organophosphorus compounds.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Aug;139(2):249-59. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23603539 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro evaluation of the catalytic activity of paraoxonases and phosphotriesterases predicts the enzyme circulatory levels required for in vivo protection against organophosphate intoxications.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Nov 25;259(Pt B):252-256. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.04.039. Epub 2016 May 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27163850 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of conformational variability of phosphotriesterase upon N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone and paraoxon binding: insights from molecular dynamics studies.Molecules. 2013 Dec 12;18(12):15501-18. doi: 10.3390/molecules181215501. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24352010 Free PMC article.
-
Organophosphate-Hydrolyzing Enzymes as First-Line of Defence Against Nerve Agent-Poisoning: Perspectives and the Road Ahead.Protein J. 2016 Dec;35(6):424-439. doi: 10.1007/s10930-016-9686-6. Protein J. 2016. PMID: 27830420 Review.
-
Applications of Microbial Organophosphate-Degrading Enzymes to Detoxification of Organophosphorous Compounds for Medical Countermeasures against Poisoning and Environmental Remediation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 17;25(14):7822. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147822. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 5000-fold increase in the specificity of a bacterial phosphotriesterase for malathion through combinatorial active site mutagenesis.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 10;9(4):e94177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094177. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24721933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeyaratnam J. Acute pesticide poisoning: a major global health problem. World Health Stat Q. 1990;43:139–44. - PubMed
-
- Sidell FR. Clinical effects of organophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitors. J Appl Toxicol. 1994;14:111–3. - PubMed
-
- Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P, Zilker T, Worek F. Correlation between red blood cell acetylcholinesterase activity and neuromuscular transmission in organophosphate poisoning. Chem Biol Interact. 2005;157–158:345–7. - PubMed
-
- Bird SB, Gaspari RJ, Dickson EW. Early death due to severe organophosphate poisoning is a centrally mediated process. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10:295–8. - PubMed
-
- Eddleston M, Singh S, Buckley N. Organophosphorus poisoning (acute) Clin Evid. 2005:1744–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous