Albinterferon Alfa-2b was not inferior to pegylated interferon-α in a randomized trial of patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 2 or 3
- PMID: 20600017
- PMCID: PMC3175757
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.062
Albinterferon Alfa-2b was not inferior to pegylated interferon-α in a randomized trial of patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 2 or 3
Abstract
Background & aims: A phase 3 active-controlled study was conducted to assess the efficacy/safety of albinterferon alfa-2b (albIFN), a novel, long-acting, genetic fusion polypeptide of recombinant human albumin and interferon alfa-2b, in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 2/3.
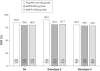
Methods: In all, 933 patients were randomized to open-label subcutaneous treatment with pegylated interferon-alfa-2a (Peg-IFNalfa-2a) 180 μg/wk, or albIFN 900 or 1200 μg every 2 weeks for 24 weeks, each administered with oral ribavirin 800 mg/day. The primary end point of the study was sustained virologic response (SVR) (HCV-RNA level, <15 IU/mL at week 48). During the study, the data monitoring committee recommended dose modification for all patients receiving albIFN 1200 μg to 900 μg, impacting 38% of this treatment arm.
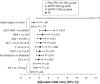
Results: By intention-to-treat analysis, SVR rates were 84.8% (95% confidence interval, 80.4%-88.6%), 79.8% (95% confidence interval, 74.9%-84.1%), and 80.0% (95% confidence interval, 75.1%-84.3%) with Peg-IFNalfa-2a, and albIFN 900 and 1200 μg, respectively. The primary hypothesis of noninferiority of SVR was established for albIFN 900 μg (P = .009) and 1200 μg (P = .006). Independent positive predictors of SVR by multivariate regression analysis were pretreatment HCV-RNA level less than 400,000 IU/mL, age younger than 45 years, body mass index less than 30 kg/m(2), genotype 2, normal γ-glutamyl transpeptidase and increased alanine aminotransferase levels at baseline, fibrosis stage F0-F2, no steatosis, and Asian geographic region (Peg-IFNalfa-2a only). The 3 treatment groups showed similar rates of serious (7%-8%) and severe (13%-16%) adverse events, and discontinuations owing to adverse events (3.6%-5.5%).
Conclusion: Albinterferon alfa-2b 900 μg every 2 weeks provides an alternative efficacious treatment option in patients with chronic HCV genotype 2 or 3.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00411385.
Copyright © 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Why do we need another interferon?Gastroenterology. 2010 Oct;139(4):1084-6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.08.015. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20800652 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lavanchy D. The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2009;29(Suppl 1):74–81. - PubMed
-
- Shepard CW, Finelli L, Alter MJ. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:558–567. - PubMed
-
- Lee CM, Lu SN, Hung CH, et al. Hepatitis C virus genotypes in southern Taiwan: prevalence and clinical implications. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006;100:767–774. - PubMed
-
- Narahari S, Juwle A, Basak S, et al. Prevalence and geographic distribution of hepatitis C virus genotypes in Indian patient cohort. Infect Genet Evol. 2009;9:643–645. - PubMed
-
- Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

