Immune response to hepatitis B vaccine in HIV-infected subjects using granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) as a vaccine adjuvant: ACTG study 5220
- PMID: 20600512
- PMCID: PMC2943846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.06.030
Immune response to hepatitis B vaccine in HIV-infected subjects using granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) as a vaccine adjuvant: ACTG study 5220
Abstract
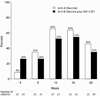
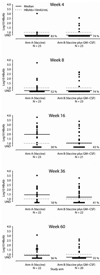
HIV-infected persons are at risk for HBV co-infection which is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Unfortunately, protective immunity following HBV vaccination in HIV-infected persons is poor. This randomized, phase II, open-label study aimed to evaluate efficacy and safety of 40 mcg HBV vaccine with or without 250 mcg GM-CSF administered at day 0, weeks 4 and 12. HIV-infected individuals >or=18 years of age, CD4 count >or=200 cells/mm(3), seronegative for HBV and HCV, and naïve to HBV vaccination were eligible. Primary endpoints were quantitative HBsAb titers and adverse events. The study enrolled 48 subjects. Median age and baseline CD4 were 41 years and 446 cells/mm(3), 37 were on ART, and 26 subjects had undetectable VL. Vaccination was well tolerated. Seven subjects in the GM-CSF arm reported transient grade >or=2 signs/symptoms (six grade 2, one grade 3), mostly aches and nausea. GM-CSF had no significant effect on VL or CD4. Four weeks after vaccination, 26 subjects (59%) developed a protective antibody response (HBsAb >or=10 mIU/mL; 52% in the GM-CSF arm and 65% in the control arm) without improved Ab titer in the GM-CSF vs. control arm (median 11 mIU/mL vs. 92 mIU/mL, respectively). Response was more frequent in those with CD4 >or=350 cells/mm(3) (64%) than with CD4 <350 cells/mm(3) (50%), though not statistically significant. GM-CSF as an adjuvant did not improve the Ab titer or the development of protective immunity to HBV vaccination in those receiving an accelerated vaccine schedule. Given the common routes of transmission for HIV and HBV, additional HBV vaccine research is warranted.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Alter M. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and HIV co-infection. J Hepatol. 2006;44:6–9. - PubMed
-
- Soriano V, Puoti M, Peters M, Benhamou Y, Sulkowski M, Zoulim F, Mauss S, Rockstroh J. Care of HIV patients with chronic hepatitis B: updated recommendations from the HIV-Hepatitis B Virus International Panel. AIDS. 2008 Jul 31;22(12):1399–1410. - PubMed
-
- Bica I, McGovern B, Dhar R, et al. Increasing mortality due to end-stage liver disease in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(3):492–497. - PubMed
-
- Mocroft A, Soriano V, Rockstroh J, Reiss P, Kirk O, de Wit S, Gatell J, Clotet B, Phillips AN, Lundgren JD EuroSIDA Study Group. Is there evidence for an increase in the death rate from liver-related disease in patients with HIV/AIDS. 2005 Dec 2;19(18):2117–2125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI 69434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR 024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI027665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI051164/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69484-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

