LP-211 is a brain penetrant selective agonist for the serotonin 5-HT(7) receptor
- PMID: 20600619
- PMCID: PMC2910240
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.06.036
LP-211 is a brain penetrant selective agonist for the serotonin 5-HT(7) receptor
Abstract
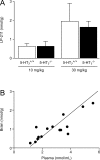
We have determined the pharmacological profile of the new serotonin 5-HT(7) receptor agonist N-(4-cyanophenylmethyl)-4-(2-diphenyl)-1-piperazinehexanamide (LP-211). Radioligand binding assays were performed on a panel of 5-HT receptor subtypes. The compound was also evaluated in vivo by examining its effect on body temperature regulation in mice lacking the 5-HT(7) receptor (5-HT(7)(-/-)) and their 5-HT(7)(+/+) sibling controls. Disposition studies were performed in mice of both genotypes. It was found that LP-211 was brain penetrant and underwent metabolic degradation to 1-(2-diphenyl)piperazine (RA-7). In vitro binding assays revealed that RA-7 possessed higher 5-HT(7) receptor affinity than LP-211 and a better selectivity profile over a panel of 5-HT receptor subtypes. In vivo it was demonstrated that LP-211, and to a lesser degree RA-7, induced hypothermia in 5-HT(7)(+/+) but not in 5-HT(7)(-/-) mice. Our results suggest that LP-211 can be used as a 5-HT(7) receptor agonist in vivo.
2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas DR, Hagan JJ. 5-HT7 receptors. Curr. Drug Target CNS Neurol. Disord. 2004;3:81–90. - PubMed
-
- Hedlund PB, Sutcliffe JG. Functional, molecular and pharmacological advances in 5-HT7 receptor research. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004;25:481–486. - PubMed
-
- Bard JA, Zgombick J, Adham N, Vaysse P, Branchek TA, Weinshank RL. Cloning of a novel human serotonin receptor (5-HT7) positively linked to adenylate cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:23422–23426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

