Th1 versus Th17: are T cell cytokines relevant in multiple sclerosis?
- PMID: 20600875
- PMCID: PMC3004998
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.05.012
Th1 versus Th17: are T cell cytokines relevant in multiple sclerosis?
Abstract
Our understanding of the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis (MS) has evolved significantly over the past two decades as the fields of immunology and neurobiology provide new avenues of exploration into the cause and mechanism of the disease. It has been known for decades that T cells have different cytokine phenotypes, yet the cytokine phenotype of pathogenic T cells in MS is still an area of debate. In EAE, it appears that IFNγ and IL-17, produced by Th1 and Th17 cells respectively, are not the critical factor that determines T cell encephalitogenicity. However, there are molecules such as IL-23, T-bet and STAT4, that appear to be critical, yet it is unclear whether all these molecules contribute to a common, yet undefined pathway, or act in a synergistic manner which culminates in encephalitogenicity has still to be determined. Therefore, the focus of research on effector T cells in MS should focus on pathways upstream of the cytokines that define Th1 and Th17 cells, since downstream products, such as IFNγ and IL-17, probably are not critical determinants of whether an effector T cells is capable of trafficking to the CNS and inducing inflammatory demyelination.
2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
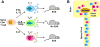
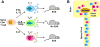
References
-
- Pettinelli CB, McFarlin DE. Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL/J mice after in vitro activation of lymph node cells by myelin basic protein: requirement for Lyt1+2- T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981;127:1420–1423. - PubMed
-
- McDonald AH, Swanborg RH. Antigen-specific inhibition of immune interferon production by suppressor cells of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1988;140:1132–1138. - PubMed
-
- Waldburger KE, Hastings RC, Schaub RG, Goldman SL, Leonard JP. Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis after in vitro treatment with recombinant murine interleukin-12. Preferential expansion of interferon-gamma-producing cells and increased expression of macrophage-associated inducible nitric oxide synthase as immunomodulatory mechanisms. Am J Pathol. 1996;148:375–382. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yura M, Takahashi I, Serada M, Koshio T, Nakagami K, Yuki Y, Kiyono H. Role of MOG-stimulated Th1 type “light up” (GFP+) CD4+ T cells for the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) J Autoimmun. 2001;17:17–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

