A spatiotemporal atlas of MR intensity, tissue probability and shape of the fetal brain with application to segmentation
- PMID: 20600970
- PMCID: PMC2930902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.054
A spatiotemporal atlas of MR intensity, tissue probability and shape of the fetal brain with application to segmentation
Abstract
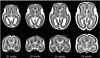
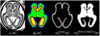
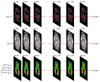
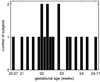
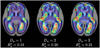
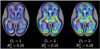
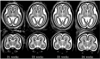
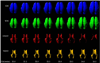
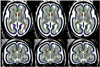
Modeling and analysis of MR images of the developing human brain is a challenge due to rapid changes in brain morphology and morphometry. We present an approach to the construction of a spatiotemporal atlas of the fetal brain with temporal models of MR intensity, tissue probability and shape changes. This spatiotemporal model is created from a set of reconstructed MR images of fetal subjects with different gestational ages. Groupwise registration of manual segmentations and voxelwise nonlinear modeling allow us to capture the appearance, disappearance and spatial variation of brain structures over time. Applying this model to atlas-based segmentation, we generate age-specific MR templates and tissue probability maps and use them to initialize automatic tissue delineation in new MR images. The choice of model parameters and the final performance are evaluated using clinical MR scans of young fetuses with gestational ages ranging from 20.57 to 24.71 weeks. Experimental results indicate that quadratic temporal models can correctly capture growth-related changes in the fetal brain anatomy and provide improvement in accuracy of atlas-based tissue segmentation.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage. 2005;26(3):839–851. - PubMed
-
- Bajcsy R, Lieberson R, Reivich M. A computerized system for the elastic matching of deformed radiographic images to idealized atlas images. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1983;7(4):618–625. - PubMed
-
- Battin MR, Maalouf EF, Counsell SJ, Herlihy AH, Rutherford MA, Azzopardi D, Edwards AD. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in very preterm infants: visualization of the germinal matrix, early myelination, and cortical folding. Pediatrics. 1998;101(6):957–962. - PubMed
-
- Davis BC, Fletcher PT, Bullitt E, Joshi SC. Population shape regression from random design data; Proc. International Conference on Computer Vision; 2007. pp. 1–7.
-
- Dice LR. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology. 1945;26(3):297–302.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

