Palmitoylome profiling reveals S-palmitoylation-dependent antiviral activity of IFITM3
- PMID: 20601941
- PMCID: PMC2928251
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.405
Palmitoylome profiling reveals S-palmitoylation-dependent antiviral activity of IFITM3
Abstract
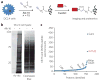
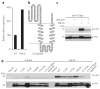
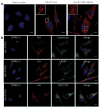
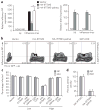
Identification of immune effectors and the post-translational modifications that control their activity is essential for dissecting mechanisms of immunity. Here we demonstrate that the antiviral activity of interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) is post-translationally regulated by S-palmitoylation. Large-scale profiling of palmitoylated proteins in a dendritic cell line using a chemical reporter strategy revealed over 150 lipid-modified proteins with diverse cellular functions, including innate immunity. We discovered that S-palmitoylation of IFITM3 on membrane-proximal cysteines controls its clustering in membrane compartments and its antiviral activity against influenza virus. The sites of S-palmitoylation are highly conserved among the IFITM family of proteins in vertebrates, which suggests that S-palmitoylation of these immune effectors may be an ancient post-translational modification that is crucial for host resistance to viral infections. The S-palmitoylation and clustering of IFITM3 will be important for elucidating its mechanism of action and for the design of antiviral therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Finlay BB, McFadden G. Anti-immunology: evasion of the host immune system by bacterial and viral pathogens. Cell. 2006;124:767–782. - PubMed
-
- Flannagan RS, Cosio G, Grinstein S. Antimicrobial mechanisms of phagocytes and bacterial evasion strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Linder ME, Deschenes RJ. Palmitoylation: policing protein stability and traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:74–84. - PubMed
-
- Charron G, Wilson J, Hang HC. Chemical tools for understanding protein lipidation in eukaryotes. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009;13:382–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

