Androgen-induced TOP2B-mediated double-strand breaks and prostate cancer gene rearrangements
- PMID: 20601956
- PMCID: PMC3157086
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.613
Androgen-induced TOP2B-mediated double-strand breaks and prostate cancer gene rearrangements
Abstract
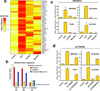
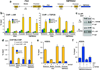
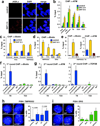
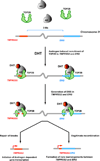
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) can lead to the development of genomic rearrangements, which are hallmarks of cancer. Fusions between TMPRSS2, encoding the transmembrane serine protease isoform 2, and ERG, encoding the v-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog, are among the most common oncogenic rearrangements observed in human cancer. We show that androgen signaling promotes co-recruitment of androgen receptor and topoisomerase II beta (TOP2B) to sites of TMPRSS2-ERG genomic breakpoints, triggering recombinogenic TOP2B-mediated DSBs. Furthermore, androgen stimulation resulted in de novo production of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion transcripts in a process that required TOP2B and components of the DSB repair machinery. Finally, unlike normal prostate epithelium, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia cells showed strong coexpression of androgen receptor and TOP2B. These findings implicate androgen-induced TOP2B-mediated DSBs in generating TMPRSS2-ERG rearrangements.
Figures



Comment in
-
On the origin of prostate fusion oncogenes.Nat Genet. 2010 Aug;42(8):647-8. doi: 10.1038/ng0810-647. Nat Genet. 2010. PMID: 20664645 No abstract available.
-
Prostate cancer: Gene fusions.Nat Rev Urol. 2010 Sep;7(9):473. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2010.125. Nat Rev Urol. 2010. PMID: 20836279 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rowley JD. Chromosomal translocations: revisited yet again. Blood. 2008;112:2183–2189. - PubMed
-
- Mitelman F, Johansson B, Mertens F. The impact of translocations and gene fusions on cancer causation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:233–245. - PubMed
-
- Morgan WF, et al. DNA double-strand breaks, chromosomal rearrangements, and genomic instability. Mutat Res. 1998;404:125–128. - PubMed
-
- Richardson C, Jasin M. Frequent chromosomal translocations induced by DNA double-strand breaks. Nature. 2000;405:697–700. - PubMed
References for Methods
-
- Wang Q, Carroll JS, Brown M. Spatial and temporal recruitment of androgen receptor and its coactivators involves chromosomal looping and polymerase tracking. Mol Cell. 2005;19:631–642. - PubMed
-
- Splinter E, Grosveld F, de Laat W. 3C technology: analyzing the spatial organization of genomic loci in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 2004;375:493–507. - PubMed
-
- DeWeese TL, et al. Human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins alter cell cycle progression but not radiosensitivity of carcinoma cells treated with low-dose-rate radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;37:145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

