Crystal structure of the conserved herpesvirus fusion regulator complex gH-gL
- PMID: 20601960
- PMCID: PMC2921994
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1837
Crystal structure of the conserved herpesvirus fusion regulator complex gH-gL
Abstract
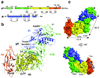
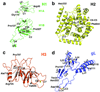
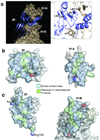
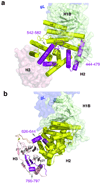
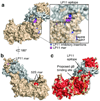
Herpesviruses, which cause many incurable diseases, infect cells by fusing viral and cellular membranes. Whereas most other enveloped viruses use a single viral catalyst called a fusogen, herpesviruses, inexplicably, require two conserved fusion-machinery components, gB and the heterodimer gH-gL, plus other nonconserved components. gB is a class III viral fusogen, but unlike other members of its class, it does not function alone. We determined the crystal structure of the gH ectodomain bound to gL from herpes simplex virus 2. gH-gL is an unusually tight complex with a unique architecture that, unexpectedly, does not resemble any known viral fusogen. Instead, we propose that gH-gL activates gB for fusion, possibly through direct binding. Formation of a gB-gH-gL complex is critical for fusion and is inhibited by a neutralizing antibody, making the gB-gH-gL interface a promising antiviral target.
Figures
References
-
- Heldwein EE, et al. Crystal structure of glycoprotein B from herpes simplex virus 1. Science. 2006;313:217–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R56 AI076231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR015301/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036731/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI018289/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI18289/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI056045/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI056045/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR-15301/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1DP20D001996/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- R01 AI056045/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI018289/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD001996/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- AI076231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

