Molecular battles between plant and pathogenic bacteria in the phyllosphere
- PMID: 20602017
- PMCID: PMC3041987
- DOI: 10.1590/s0100-879x2010007500060
Molecular battles between plant and pathogenic bacteria in the phyllosphere
Abstract
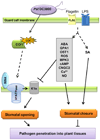
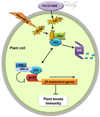
The phyllosphere, i.e., the aerial parts of the plant, provides one of the most important niches for microbial colonization. This niche supports the survival and, often, proliferation of microbes such as fungi and bacteria with diverse lifestyles including epiphytes, saprophytes, and pathogens. Although most microbes may complete the life cycle on the leaf surface, pathogens must enter the leaf and multiply aggressively in the leaf interior. Natural surface openings, such as stomata, are important entry sites for bacteria. Stomata are known for their vital role in water transpiration and gas exchange between the plant and the environment that is essential for plant growth. Recent studies have shown that stomata can also play an active role in limiting bacterial invasion of both human and plant pathogenic bacteria as part of the plant innate immune system. As counter-defense, plant pathogens such as Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato (Pst) DC3000 use the virulence factor coronatine to suppress stomate-based defense. A novel and crucial early battleground in host-pathogen interaction in the phyllosphere has been discovered with broad implications in the study of bacterial pathogenesis, host immunity, and molecular ecology of bacterial diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato exploits light signals to optimize virulence and colonization of leaves.Environ Microbiol. 2018 Dec;20(12):4261-4280. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14331. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30058114
-
Role of stomata in plant innate immunity and foliar bacterial diseases.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2008;46:101-22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.121107.104959. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2008. PMID: 18422426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Closely related NAC transcription factors of tomato differentially regulate stomatal closure and reopening during pathogen attack.Plant Cell. 2014 Jul;26(7):3167-84. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.128272. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25005917 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic screen reveals Arabidopsis stomatal and/or apoplastic defenses against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002291. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002291. Epub 2011 Oct 6. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21998587 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000: a model pathogen for probing disease susceptibility and hormone signaling in plants.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013;51:473-98. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102321. Epub 2013 May 31. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013. PMID: 23725467 Review.
Cited by
-
Oligo-DNA custom macroarray for monitoring major pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungi and bacteria in the phyllosphere of apple trees.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034249. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479577 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of disease severity on the structure and diversity of the phyllosphere microbial community in tobacco.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1081576. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1081576. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36687583 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory Peptides as Bullets: Effector Peptides from Pathogens against Antimicrobial Peptides from Soybean.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 5;21(23):9294. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239294. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33291499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomics profiling revealed multi-stress responsive roles of the CC-NBS-LRR genes in three mango cultivars.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 30;14:1285547. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1285547. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37965009 Free PMC article.
-
The Lifecycle of the Plant Immune System.CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2020;39(1):72-100. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2020.1757829. Epub 2020 May 18. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33343063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrios GN. Plant pathology. 5th edn. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press; 2005.
-
- Andrews JH, Harris RF. The ecology and biogeography of microorganisms on plant surfaces. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2000;38:145–180. - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

