Exhaustive exercise reduces TNF-α and IFN-α production in response to R-848 via toll-like receptor 7 in mice
- PMID: 20602110
- PMCID: PMC7088253
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-010-1560-1
Exhaustive exercise reduces TNF-α and IFN-α production in response to R-848 via toll-like receptor 7 in mice
Abstract
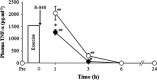
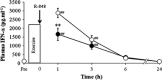
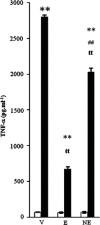
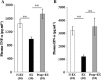
Stressful exercise results in temporary immune depression. However, the impact of exercise on the immune responses via toll-like receptor (TLR) 7, which recognizes the common viral genomic feature, single-stranded RNA, remains unclear. To clarify the effect of stressful exercise on immune function in response to viral infection, we measured the changes in the plasma concentration of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interferon (IFN)-α, which are induced downstream from the TLR-ligand interaction, in exhaustive-exercised mice immediately after treatment with the imidazoquinoline R-848, which can bind to and activate TLR7. Both exhaustive-exercised (EX) and non-exercised (N-EX) male C3H/HeN mice were injected with R-848 (5 mg kg(-1)), and blood samples were collected. In addition, RAW264 cells, which are mouse macrophage cells, were cultured 30 min after epinephrine (10 μM) or norepinephrine (10 μM) treatments, and were then stimulated with R-848 (10 μg ml(-1)). In addition, the effect of propranolol (10 mg kg(-1)) as blockade of β-adrenergic receptors on R-848-induced TNF-α and IFN-α production in the exercised mice was examined. Both the TNF-α and IFN-α concentrations in the plasma of EX were significantly lower than those in the plasma of N-EX after R-848 injection (P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively), although the R-848 treatment increased the plasma TNF-α and IFN-α concentrations in both groups (P < 0.01, respectively). The R-848-induced TNF-α production in RAW264 cells was significantly inhibited by epinephrine and norepinephrine pre-treatment, although IFN-α was not detected. The propranolol treatment completely inhibited exercise-induced TNF-α and IFN-α suppression in response to R-848 in the mice. These data suggest that EX induces a reduction in TNF-α and IFN-α production in response to R-848, and that these phenomena might be regulated by an exercise-induced elevation of the systemic catecholamines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon-beta, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, production in response to poly I:C is maintained despite exhaustive exercise in mice.J Physiol Sci. 2012 Jan;62(1):59-62. doi: 10.1007/s12576-011-0177-4. Epub 2011 Oct 4. J Physiol Sci. 2012. PMID: 21968540 Free PMC article.
-
Exhaustive exercise increases the TNF-α production in response to flagellin via the upregulation of toll-like receptor 5 in the large intestine in mice.Immunol Lett. 2014 Mar-Apr;158(1-2):151-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.12.021. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Immunol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24412598
-
Exhaustive exercise reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in response to lipopolysaccharide in mice.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2010;17(4):279-86. doi: 10.1159/000290044. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2010. PMID: 20203534
-
The early induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 and the downregulation of toll-like receptors 7 and 9 induce tolerance in costimulated macrophages.Mol Cells. 2015 Jan 31;38(1):26-32. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.2136. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Mol Cells. 2015. PMID: 25518931 Free PMC article.
-
PTPN22 Variant R620W Is Associated With Reduced Toll-like Receptor 7-Induced Type I Interferon in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Sep;67(9):2403-14. doi: 10.1002/art.39211. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26018863
Cited by
-
Sparassis crispa Intake Improves the Reduced Lipopolysaccharide-Induced TNF-α Production That Occurs upon Exhaustive Exercise in Mice.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 2;11(9):2049. doi: 10.3390/nu11092049. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31480668 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate lifelong overexpression of tuberous sclerosis complex 1 (TSC1) improves health and survival in mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 11;7(1):834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00970-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28400571 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-beta, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, production in response to poly I:C is maintained despite exhaustive exercise in mice.J Physiol Sci. 2012 Jan;62(1):59-62. doi: 10.1007/s12576-011-0177-4. Epub 2011 Oct 4. J Physiol Sci. 2012. PMID: 21968540 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like Receptors in Immuno-Metabolic Regulation of Emotion and Memory.Cells. 2025 Jun 19;14(12):933. doi: 10.3390/cells14120933. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40558558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphocyte glucose and glutamine metabolism as targets of the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of exercise.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:326803. doi: 10.1155/2014/326803. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24987195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bagby GJ, Sawaya DE, Crouch LD, Shepherd RE. Prior exercise suppresses the plasma tumor necrosis factor response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Appl Physiol. 1994;77:1542–1547. - PubMed
-
- Ceddia MA, Woods JA. Exercise suppresses macrophage antigen presentation. J Appl Physiol. 1999;87:2253–2258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

