A kinesin motor in a force-producing conformation
- PMID: 20602775
- PMCID: PMC2906495
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-10-19
A kinesin motor in a force-producing conformation
Abstract
Background: Kinesin motors hydrolyze ATP to produce force and move along microtubules, converting chemical energy into work by a mechanism that is only poorly understood. Key transitions and intermediate states in the process are still structurally uncharacterized, and remain outstanding questions in the field. Perturbing the motor by introducing point mutations could stabilize transitional or unstable states, providing critical information about these rarer states.
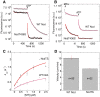
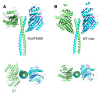
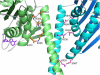
Results: Here we show that mutation of a single residue in the kinesin-14 Ncd causes the motor to release ADP and hydrolyze ATP faster than wild type, but move more slowly along microtubules in gliding assays, uncoupling nucleotide hydrolysis from force generation. A crystal structure of the motor shows a large rotation of the stalk, a conformation representing a force-producing stroke of Ncd. Three C-terminal residues of Ncd, visible for the first time, interact with the central beta-sheet and dock onto the motor core, forming a structure resembling the kinesin-1 neck linker, which has been proposed to be the primary force-generating mechanical element of kinesin-1.
Conclusions: Force generation by minus-end Ncd involves docking of the C-terminus, which forms a structure resembling the kinesin-1 neck linker. The mechanism by which the plus- and minus-end motors produce force to move to opposite ends of the microtubule appears to involve the same conformational changes, but distinct structural linkers. Unstable ADP binding may destabilize the motor-ADP state, triggering Ncd stalk rotation and C-terminus docking, producing a working stroke of the motor.
Figures
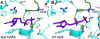

Similar articles
-
A lever-arm rotation drives motility of the minus-end-directed kinesin Ncd.Nature. 2006 Feb 16;439(7078):875-8. doi: 10.1038/nature04320. Epub 2005 Dec 28. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16382238 Free PMC article.
-
Rotation of the stalk/neck and one head in a new crystal structure of the kinesin motor protein, Ncd.EMBO J. 2003 Oct 15;22(20):5382-9. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg531. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 14532111 Free PMC article.
-
A metal switch for controlling the activity of molecular motor proteins.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Dec 25;19(1):122-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2190. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22198464 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin motors as molecular machines.Bioessays. 2003 Dec;25(12):1212-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.10358. Bioessays. 2003. PMID: 14635256 Review.
-
Review: Mechanochemistry of the kinesin-1 ATPase.Biopolymers. 2016 Aug;105(8):476-82. doi: 10.1002/bip.22862. Biopolymers. 2016. PMID: 27120111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A seesaw model for intermolecular gating in the kinesin motor protein.Biophys Rev. 2011 Jun;3(2):85-100. doi: 10.1007/s12551-011-0049-4. Epub 2011 Jun 4. Biophys Rev. 2011. PMID: 21765878 Free PMC article.
-
ATP synthase: the right size base model for nanomotors in nanomedicine.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Jan 29;2014:567398. doi: 10.1155/2014/567398. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24605056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote control of myosin and kinesin motors using light-activated gearshifting.Nat Nanotechnol. 2014 Sep;9(9):693-7. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.147. Epub 2014 Aug 3. Nat Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25086603 Free PMC article.
-
Neck-motor interactions trigger rotation of the kinesin stalk.Sci Rep. 2012;2:236. doi: 10.1038/srep00236. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22355749 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of dynein heavy chain mutations reveal complex interactions between dynein motor domains and cellular dynein functions.Genetics. 2012 Aug;191(4):1157-79. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.141580. Epub 2012 May 29. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22649085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howard J. Mechanics of motor proteins and the cytoskeleton. 1. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, Inc; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

