Development of admixture mapping panels for African Americans from commercial high-density SNP arrays
- PMID: 20602785
- PMCID: PMC2996945
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-417
Development of admixture mapping panels for African Americans from commercial high-density SNP arrays
Abstract
Background: Admixture mapping is a powerful approach for identifying genetic variants involved in human disease that exploits the unique genomic structure in recently admixed populations. To use existing published panels of ancestry-informative markers (AIMs) for admixture mapping, markers have to be genotyped de novo for each admixed study sample and samples representing the ancestral parental populations. The increased availability of dense marker data on commercial chips has made it feasible to develop panels wherein the markers need not be predetermined.
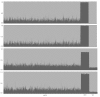
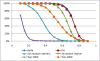
Results: We developed two panels of AIMs (approximately 2,000 markers each) based on the Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 for admixture mapping with African American samples. These two AIM panels had good map power that was higher than that of a denser panel of approximately 20,000 random markers as well as other published panels of AIMs. As a test case, we applied the panels in an admixture mapping study of hypertension in African Americans in the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area.
Conclusions: Developing marker panels for admixture mapping from existing genome-wide genotype data offers two major advantages: (1) no de novo genotyping needs to be done, thereby saving costs, and (2) markers can be filtered for various quality measures and replacement markers (to minimize gaps) can be selected at no additional cost. Panels of carefully selected AIMs have two major advantages over panels of random markers: (1) the map power from sparser panels of AIMs is higher than that of approximately 10-fold denser panels of random markers, and (2) clusters can be labeled based on information from the parental populations. With current technology, chip-based genome-wide genotyping is less expensive than genotyping approximately 20,000 random markers. The major advantage of using random markers is the absence of ascertainment effects resulting from the process of selecting markers. The ability to develop marker panels informative for ancestry from SNP chip genotype data provides a fresh opportunity to conduct admixture mapping for disease genes in admixed populations when genome-wide association data exist or are planned.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ancestry informative marker panels for African Americans based on subsets of commercially available SNP arrays.Genet Epidemiol. 2011 Jan;35(1):80-3. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20550. Genet Epidemiol. 2011. PMID: 21181899 Free PMC article.
-
Selecting SNPs informative for African, American Indian and European Ancestry: application to the Family Investigation of Nephropathy and Diabetes (FIND).BMC Genomics. 2016 May 4;17:325. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2654-x. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27142425 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestry-informative markers for African Americans based on the Affymetrix Pan-African genotyping array.PeerJ. 2014 Nov 4;2:e660. doi: 10.7717/peerj.660. eCollection 2014. PeerJ. 2014. PMID: 25392759 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for admixture mapping of complex traits.Am J Hum Genet. 2005 Jan;76(1):1-7. doi: 10.1086/426949. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Am J Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15540159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic admixture: a tool to identify diabetic nephropathy genes in African Americans.Ethn Dis. 2008 Summer;18(3):384-8. Ethn Dis. 2008. PMID: 18785456 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Ancestry Inference and Its Application for the Genetic Mapping of Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 28;22(13):6962. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136962. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extensive set of African ancestry-informative markers (AIMs) to study ancestry and population health.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 23;14:1061781. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1061781. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36911410 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating population stratification and admixture using eigenanalysis of dense genotypes.Heredity (Edinb). 2011 Oct;107(5):413-20. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2011.26. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Heredity (Edinb). 2011. PMID: 21448230 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ancestry is associated with measures of subclinical atherosclerosis in African Americans: the Jackson Heart Study.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 May;35(5):1271-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304855. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25745061 Free PMC article.
-
The Biorepository and Integrative Genomics resource for inclusive genomics: insights from a diverse pediatric and admixed cohort.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 26:2025.01.03.25319944. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.03.25319944. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39802793 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

