Decreased expression of GRAF1/OPHN-1-L in the X-linked alpha thalassemia mental retardation syndrome
- PMID: 20602808
- PMCID: PMC2915949
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-3-28
Decreased expression of GRAF1/OPHN-1-L in the X-linked alpha thalassemia mental retardation syndrome
Abstract
Background: ATRX is a severe X-linked disorder characterized by mental retardation, facial dysmorphism, urogenital abnormalities and alpha-thalassemia. The disease is caused by mutations in ATRX gene, which encodes a protein belonging to the SWI/SNF DNA helicase family, a group of proteins involved in the regulation of gene transcription at the chromatin level. In order to identify specific genes involved in the pathogenesis of the disease, we compared, by cDNA microarray, the expression levels of approximately 8500 transcripts between ATRX and normal males of comparable age.
Methods: cDNA microarray was performed using total RNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of ATRX and normal males. Microarray results were validated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
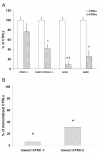
Results: cDNA microarray analysis showed that 35 genes had a lower expression (30-35% of controls) while 25 transcripts had a two-fold higher expression in comparison to controls. In the microarray results the probe for oligophrenin-1, a gene known for its involvement in mental retardation, showed a decreased hybridization signal. However, such gene was poorly expressed in blood mononuclear cells and its decrease was not confirmed in the quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay. On the other hand, the expression of an homologous gene, the GTPase regulator associated with the focal adhesion kinase 1/Oligophrenin-1-like (GRAF1/OPHN-1-L), was relatively high in blood mononuclear cells and significantly decreased in ATRX patients. The analysis of the expression pattern of the GRAF1/OPHN-1-L gene in human tissues and organs revealed the predominant brain expression of a novel splicing isoform, called variant-3.
Conclusions: Our data support the hypothesis of a primary role for altered gene expression in ATRX syndrome and suggest that the GRAF1/OPHN-1-L gene might be involved in the pathogenesis of the mental retardation. Moreover a novel alternative splicing transcript of such gene, predominantly expressed in brain tissues, was identified.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Clinical feature and genetic analysis of a case of X-linked alpha-thalassemia mental retardation syndrome neonate caused by ATRX gene variant and literature review].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Feb 10;42(2):162-169. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20240126-00074. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40350394 Review. Chinese.
-
Identification of a Novel Frameshift variant of the ATRX gene: a Case Report and Review of the genotype-phenotype relationship.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Oct 3;24(1):631. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05088-0. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39363269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATRX encodes a novel member of the SNF2 family of proteins: mutations point to a common mechanism underlying the ATR-X syndrome.Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Dec;5(12):1899-907. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.12.1899. Hum Mol Genet. 1996. PMID: 8968741
-
A novel missense mutation in ATRX uncovered in a Yemeni family leads to alpha-thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome without alpha-thalassemia.Ir J Med Sci. 2017 May;186(2):333-337. doi: 10.1007/s11845-016-1418-6. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Ir J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 26860117
-
Determination of the genomic structure of the XNP/ATRX gene encoding a potential zinc finger helicase.Genomics. 1997 Jul 15;43(2):149-55. doi: 10.1006/geno.1997.4793. Genomics. 1997. PMID: 9244431
Cited by
-
ADAR1 regulates ARHGAP26 gene expression through RNA editing by disrupting miR-30b-3p and miR-573 binding.RNA. 2013 Nov;19(11):1525-36. doi: 10.1261/rna.041533.113. Epub 2013 Sep 25. RNA. 2013. PMID: 24067935 Free PMC article.
-
GRAF1a is a brain-specific protein that promotes lipid droplet clustering and growth, and is enriched at lipid droplet junctions.J Cell Sci. 2014 Nov 1;127(Pt 21):4602-19. doi: 10.1242/jcs.147694. Epub 2014 Sep 4. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25189622 Free PMC article.
-
Carnosine Prevents Aβ-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Microglial Cells: A Key Role of TGF-β1.Cells. 2019 Jan 17;8(1):64. doi: 10.3390/cells8010064. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30658430 Free PMC article.
-
Basic concepts of epigenetics: impact of environmental signals on gene expression.Epigenetics. 2012 Feb;7(2):119-30. doi: 10.4161/epi.7.2.18764. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 22395460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Pro-Oxidant and Pro-Inflammatory Activities of M1 Macrophages by the Natural Dipeptide Carnosine.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 25;21(3):776. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030776. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31991717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aapola U, Shibuya K, Scott HS, Ollila J, Vihinen M, Heino M, Shintani A, Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Krohn K, Antonarakis SE, Shimizu N, Kudoh J, Peterson P. Isolation and Initial Characterization of a Novel Zinc Finger Gene, DNMT3L, on 21q22.3, Related to the Cytosine-5-Methyltransferase 3 Gene Family. Genomics. 2000;65:293–298. doi: 10.1006/geno.2000.6168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Argentaro A, Yang JC, Chapman L, Kowalczyk MS, Gibbons RJ, Higgs DR, Neuhaus D, Rhodes D. Structural consequences of disease-causing mutations in the ATRX-DNMT3-DNMT3L (ADD) domain of the chromatin-associated protein ATRX. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(29):11939–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704057104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

