Environmental and genetic activation of a brain-adipocyte BDNF/leptin axis causes cancer remission and inhibition
- PMID: 20603014
- PMCID: PMC3784009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.05.029
Environmental and genetic activation of a brain-adipocyte BDNF/leptin axis causes cancer remission and inhibition
Abstract
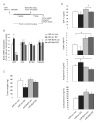
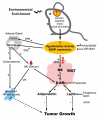
Cancer is influenced by its microenvironment, yet broader, environmental effects also play a role but remain poorly defined. We report here that mice living in an enriched housing environment show reduced tumor growth and increased remission. We found this effect in melanoma and colon cancer models, and that it was not caused by physical activity alone. Serum from animals held in an enriched environment (EE) inhibited cancer proliferation in vitro and was markedly lower in leptin. Hypothalamic brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was selectively upregulated by EE, and its genetic overexpression reduced tumor burden, whereas BDNF knockdown blocked the effect of EE. Mechanistically, we show that hypothalamic BDNF downregulated leptin production in adipocytes via sympathoneural beta-adrenergic signaling. These results suggest that genetic or environmental activation of this BDNF/leptin axis may have therapeutic significance for cancer.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Enriching stress research.Cell. 2010 Jul 9;142(1):15-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.025. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20603008
-
Neuroendocrinology: Housing conditions affect tumour growth.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010 Sep;11(9):613. doi: 10.1038/nrn2902. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20803794 No abstract available.
-
Macroenvironment: Stimulating resistance.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Sep;10(9):600. doi: 10.1038/nrc2925. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20803812 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aaronson SA. Growth factors and cancer. Science. 1991;254:1146–1153. - PubMed
-
- Barb D, Williams C, Neuwirth AK, Mantzoros CS. Adiponectin in relation to malignancies: a review of existing basic research and clinical evidence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007;86:858s–866s. - PubMed
-
- Bariohay B, Lebrun B, Moyse E, Jean A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor pays a role as an anorexigenic factor in the dorsal vagal complex. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5612–5620. - PubMed
-
- Benaroya-Milshtein N, Hollander N, Apter A, Kukulansky T, Raz N, Wilf A, Yaniv I, Pick CG. Environmental enrichment in mice decrease anxiety, attenuates stress responses and enhances natural killer cell activity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004;20:1341–1347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

