Stromal interleukin-1 expression in the cornea after haze-associated injury
- PMID: 20603114
- PMCID: PMC2952405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.06.023
Stromal interleukin-1 expression in the cornea after haze-associated injury
Abstract
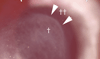
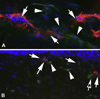
The purpose of this study was to determine whether myofibroblasts or other cells in the stroma in the cornea produce interleukin (IL)-1alpha or IL-1beta that could modulate myofibroblast viability in corneas with haze after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK). Twenty-four female rabbits had haze-generating PRK for 9 diopters of myopia and were sacrificed at 1 week, 2 weeks, 3 weeks or 4 weeks after surgery. Corneal rims were removed, frozen in OCT at -80 degrees C, and analyzed by immunocytochemistry using primary antibodies to IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and alpha smooth muscle actin (SMA). Double immunostaining was performed for the co-localization of SMA with IL-1alpha or IL-1beta. Central dense haze and peripheral slight haze regions of each cornea were analyzed. SMA+ cells that expressed IL-1alpha protein were detected in both regions of the corneas at most time points following PRK. However, in the haze region at the 1, 3 and 4 week time points, significantly more (p<0.01) SMA+ cells did not express IL-1alpha. Also, in the haze region at all three time points, significantly more (p<0.01) SMA- cells than SMA+ cells expressed interleukin-1alpha protein. IL-1beta expression patterns in SMA+ and SMA- stromal cells was similar to that of IL-1alpha after PRK. Previous studies have demonstrated that IL-1alpha or IL-1beta triggers myofibroblast apoptosis in vitro, depending on the available concentration of apoptosis-suppressive TGFbeta. This study demonstrates that SMA- cells such as corneal fibroblasts, keratocytes, or inflammatory cells may produce IL-1alpha and/or IL-1beta that could act in paracrine fashion to regulate myofibroblast apoptosis--especially in the region where there is haze in the cornea after PRK was performed and SMA+ myofibroblasts are present at higher density. However, some SMA+ myofibroblasts themselves produce IL-1alpha and/or IL-1beta, suggesting that myofibroblast viability could also be regulated via autocrine mechanisms.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stromal haze, myofibroblasts, and surface irregularity after PRK.Exp Eye Res. 2006 May;82(5):788-97. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.09.021. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Exp Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 16303127 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal myofibroblast viability: opposing effects of IL-1 and TGF beta1.Exp Eye Res. 2009 Aug;89(2):152-8. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.03.001. Epub 2009 Mar 12. Exp Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19285499 Free PMC article.
-
A novel method for generating corneal haze in anterior stroma of the mouse eye with the excimer laser.Exp Eye Res. 2008 Feb;86(2):235-40. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.10.014. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Exp Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18068702 Free PMC article.
-
The corneal fibrosis response to epithelial-stromal injury.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jan;142:110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.09.012. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26675407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological effects of mitomycin C on late corneal haze stromal fibrosis following PRK.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Nov;200:108218. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108218. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32905844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Corneal wound healing.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Aug;197:108089. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108089. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32553485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and extracellular matrix modulation of corneal stromal opacity.Exp Eye Res. 2014 Dec;129:151-60. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.09.013. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Exp Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 25281830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corneal myofibroblasts and fibrosis.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Dec;201:108272. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108272. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 33010289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Review of Amniotic Membrane Transplantation in Ocular Surface Repair: Unveiling the Immunoregulatory Pathways for Timely Intervention.Ophthalmol Ther. 2025 Jul;14(7):1385-1409. doi: 10.1007/s40123-025-01143-w. Epub 2025 May 14. Ophthalmol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40360962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1 and Transforming Growth Factor Beta: Commonly Opposing, but Sometimes Supporting, Master Regulators of the Corneal Wound Healing Response to Injury.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Apr 1;62(4):8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.4.8. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33825855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonner JC, Lindroos PM, Rice AB, Moomaw CR, Morgan DL. Induction of PDGF receptor-alpha in rat myofibroblasts during pulmonary fibro genesis in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 1998;274:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Jester JV, Huang J, Barry-Lane PA, Kao WW, Petroll WM, Cavanaugh HD. Transforming growth factor (beta)- mediated corneal myofibroblast differentiation requires actin and fibronectin assembly. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999b;40:1959–1967. - PubMed
-
- Jester JV, Huang J, Petroll WM, Cavanaugh HD. TGF beta induced myofibroblast differentiation of rabbit keratocytes requires synergistic TGF beta, PDGF and integrin signaling. Exp. Eye Res. 2002;75:645–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

